On-Page SEO Factors for Better Rankings
If you’re looking to boost your website’s search engine rankings and attract more organic traffic, you’ve come to the right place. In this blog, we’re diving into the essential on-page SEO factors that can make or break your SEO game.
Understanding on-page SEO isn’t just about stuffing keywords into your content; it’s about creating a holistic, user-friendly experience that search engines love. And who better to guide us than the SEO maestro himself, Koray Tuğberk GÜBÜR? We’ll be exploring his insights on Semantic/Holistic SEO and how to implement these strategies effectively.
Credits to LinkedIn
Understanding On-Page SEO
Before we dive into the nitty-gritty details, let’s get a solid grasp of what on-page SEO is all about. Simply put, on-page SEO refers to the practice of optimizing individual web pages to rank higher and earn more relevant traffic in search engines. It encompasses various elements within your control, such as content, HTML source code, and user experience.
On-page SEO plays a crucial role in improving search engine rankings by ensuring that your website is not only user-friendly but also search engine-friendly. This involves a mix of technical and creative strategies aimed at aligning your website with the ever-evolving algorithms of search engines like Google. By focusing on on-page SEO, you’re essentially laying the groundwork for better visibility, increased traffic, and ultimately, higher conversion rates.

But there’s more to it than just keywords and meta tags. Enter Semantic/Holistic SEO, a concept championed by Koray Tuğberk GÜBÜR. This approach takes on-page SEO to the next level by emphasizing the importance of context, user intent, and comprehensive content. Instead of merely targeting specific keywords, Semantic SEO focuses on covering topics thoroughly and answering users’ questions more effectively.

So, why is on-page SEO important? Because it ensures that your content is not only discoverable but also valuable to your audience. It’s about creating a seamless experience that satisfies both users and search engines, paving the way for sustained growth and success in the digital landscape.
Key On-Page SEO Factors
Alright, folks, let’s get into the meat and potatoes of on-page SEO. Here are the key factors you need to focus on to improve your rankings and make Google (and your users) happy.
1. High-Quality Content Content is still king, but it’s got to be more than just good—it needs to be great. We’re talking about in-depth, informative, and engaging content that satisfies user intent. Here’s how you can nail it:
- Keyword Research: Use tools like Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, or SEMrush to find keywords that your audience is searching for.
- Content Relevance: Ensure your content answers the questions and needs of your audience.
- Comprehensive Coverage: Go beyond surface-level information. Cover the topic thoroughly to position yourself as an authority.
2. Title Tags The title tag is your first impression in search results. Make it count:
- Keyword Placement: Include your primary keyword, preferably near the beginning.
- Length: Keep it under 60 characters to ensure it’s fully visible in search results.
- Compelling: Write a title that grabs attention and invites clicks.
3. Meta Descriptions While meta descriptions don’t directly influence rankings, they impact click-through rates:
- Clear and Concise: Summarize the content of the page in 150-160 characters.
- Include Keywords: Use your main keyword naturally.
- Call to Action: Encourage users to click through to your site.
4. Header Tags (H1, H2, H3, etc.) Headers help structure your content and make it easier to read:
- H1 Tag: This should be your main title and include the primary keyword.
- Subheaders: Use H2 and H3 tags to break up content and include secondary keywords.
5. URL Structure Your URLs should be clean, concise, and include your target keywords:
- Descriptive: Make sure your URLs give a clear idea of the content.
- Readability: Keep them short and avoid unnecessary numbers or characters.
6. Internal Linking Internal links help distribute page authority and guide users through your site:
- Relevant Links: Link to related content that adds value for the reader.
- Anchor Text: Use descriptive and keyword-rich anchor text.
7. Image Optimization Images can boost engagement, but they need to be optimized:
- Alt Text: Describe the image with relevant keywords.
- File Size: Compress images to improve load times.
- File Names: Use descriptive, keyword-rich file names.
8. Mobile Friendliness With mobile traffic surpassing desktop, your site must be mobile-friendly:
- Responsive Design: Ensure your site looks great on all devices.
- Mobile Usability: Check for issues like buttons too close together or content wider than the screen.
9. Page Speed Page speed is a crucial ranking factor:
- Optimize Images: Compress and resize images.
- Minify Code: Reduce the size of your CSS, HTML, and JavaScript files.
- Leverage Browser Caching: Store static files to speed up load times.
10. User Experience (UX) A positive user experience keeps visitors on your site longer:
- Navigation: Make it easy for users to find what they’re looking for.
- Readability: Use legible fonts, sufficient spacing, and clear calls to action.
- Engagement: Incorporate interactive elements like videos, infographics, and polls.
11. Schema Markup Schema markup helps search engines understand your content better and can enhance your search results with rich snippets:
- Structured Data: Add schema markup to your HTML to provide context to search engines.
By focusing on these key on-page SEO factors, you’re setting your site up for success. Remember, it’s not about tricking the search engines; it’s about providing a valuable, seamless experience for your users.
Keyword Research and Optimization
Alright, now that we’ve covered the essentials, let’s dig into the heart of on-page SEO: keyword research and optimization. This is where the magic begins, folks. Without proper keywords, even the best content can remain undiscovered. So, let’s break it down.

Importance of Keyword Research
Keyword research is the foundation of any successful SEO strategy. It’s all about understanding what your audience is searching for and creating content that meets their needs. Here’s why it’s crucial:
- Audience Insight: Keywords give you direct insight into your audience’s needs, problems, and questions.
- Content Direction: Helps you create relevant and targeted content that ranks well and satisfies user intent.
- Competitive Advantage: By identifying less competitive keywords, you can carve out a niche and dominate it.
Best Practices for Keyword Research
- Start with Seed Keywords
- Brainstorming: Begin with broad terms related to your niche.
- Tools: Use tools like Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Ubersuggest to expand your list.
- Understand User Intent
- Informational: Users are looking for information (e.g., “how to bake a cake”).
- Navigational: Users are trying to find a specific site (e.g., “Facebook login”).
- Transactional: Users are looking to make a purchase (e.g., “buy running shoes online”).
- Analyze Competitors
- Identify Gaps: See what keywords your competitors are ranking for and find opportunities they may have missed.
- Content Ideas: Get inspiration for content topics and formats that perform well.
- Long-Tail Keywords
- Specificity: Long-tail keywords are longer, more specific phrases that often have less competition.
- Conversion: These keywords usually have higher conversion rates because they indicate clear intent.
- Use Keyword Research Tools
- Volume and Difficulty: Look for keywords with a good balance of search volume and competition.
- Related Keywords: Find related terms to cover your topic comprehensively.
Best Practices for Keyword Optimization
- Place Keywords Strategically
- Title Tag: Include your primary keyword near the beginning of the title tag.
- Meta Description: Naturally incorporate your main keyword.
- Headings (H1, H2, H3): Use keywords in your headings to structure your content.
- Introduction: Mention your primary keyword within the first 100 words.
- Body Content: Distribute keywords naturally throughout the content.
- Maintain Keyword Density
- Avoid Overstuffing: Keyword stuffing can lead to penalties. Aim for a natural keyword density, typically around 1-2%.
- Synonyms and LSI Keywords: Use related terms and synonyms to enrich your content without overusing your main keyword.
- Optimize Images
- Alt Text: Describe images with relevant keywords.
- File Names: Name your image files descriptively, using keywords where appropriate.
- Internal Links
- Anchor Text: Use keyword-rich anchor text for internal links to relevant pages.
- Content Relevance
- User Intent: Ensure your content matches the intent behind the keyword.
- Comprehensiveness: Cover the topic thoroughly to provide value and increase your chances of ranking.
- Regular Updates
- Content Freshness: Keep your content up to date by periodically revisiting and revising your keyword strategy.
Identifying High-Value Keywords
Now that we’ve covered the basics of keyword research and optimization, let’s zero in on identifying high-value keywords. These are the keywords that not only drive traffic but also align closely with your content and resonate with your audience. Here’s how you can pinpoint those golden keywords.

Steps to Identify High-Value Keywords
- Understand Your Niche and Audience
- Know Your Audience: Create detailed buyer personas to understand their interests, pain points, and search behaviors.
- Niche Analysis: Identify the specific areas within your niche where you can provide unique value.
- Brainstorm Seed Keywords
- Initial Ideas: Start with broad terms related to your niche. Think about the core topics your website covers.
- Customer Questions: What questions do your customers frequently ask? These can be great starting points.
- Use Keyword Research Tools
- Google Keyword Planner: Provides keyword ideas and data on search volume and competition.
- Ahrefs/SEMrush/Ubersuggest: Offer insights into keyword difficulty, search volume, and competitor analysis.
- Evaluate Keyword Metrics
- Search Volume: Look for keywords with sufficient search volume to drive traffic.
- Keyword Difficulty (KD): Assess the competition for each keyword. Lower KD means easier to rank for.
- Cost Per Click (CPC): High CPC keywords often indicate high commercial intent and value.
- Analyze User Intent
- Informational Keywords: Keywords that users search for to gain information (e.g., “how to plant tomatoes”).
- Navigational Keywords: Keywords used to find a specific website or page (e.g., “Facebook login”).
- Transactional Keywords: Keywords with the intent to make a purchase or complete a transaction (e.g., “buy running shoes”).
- Commercial Investigation Keywords: Keywords used by users looking to compare products or services (e.g., “best DSLR cameras 2024”).
- Long-Tail Keywords
- Specific Phrases: These are longer, more specific keywords that often have less competition and higher conversion rates (e.g., “best gluten-free pizza recipes”).
- Audience Focus: Long-tail keywords tend to align closely with user intent, making them valuable for targeting specific queries.
- Competitive Analysis
- Competitor Keywords: Use tools to identify the keywords your competitors are ranking for.
- Content Gaps: Find keywords that your competitors haven’t covered extensively.
- Leverage Google Search Features
- Autocomplete: Use Google’s autocomplete feature to see what related searches come up as you type your keywords.
- People Also Ask: Look at the “People Also Ask” section for more keyword ideas.
- Related Searches: Check the related searches at the bottom of the search results page for additional keywords.
- Check Search Trends
- Google Trends: Identify seasonal trends and see how keyword popularity changes over time.
Practical Example
Let’s say you run a blog about home gardening. Here’s a step-by-step example of identifying high-value keywords:
- Seed Keywords: Start with broad terms like “home gardening,” “vegetable gardening,” and “indoor plants.”
- Keyword Research Tools: Use tools like Ahrefs to find related keywords. You might discover terms like “best soil for vegetable gardening” or “how to care for indoor plants.”
- Evaluate Metrics: Look at search volume and keyword difficulty. “Best soil for vegetable gardening” might have moderate search volume and low competition, making it a high-value keyword.
- Analyze Intent: Determine that “best soil for vegetable gardening” is an informational keyword with potential commercial value if you can link to soil products.
- Long-Tail Keywords: Find more specific phrases like “best organic soil for vegetable gardening in small spaces.”
- Competitive Analysis: Check your competitors’ content on this topic. Identify gaps or areas where you can provide more value.
- Google Search Features: Use Google autocomplete to see related searches like “best soil for tomato plants” and “best soil for container gardening.”
Strategic Keyword Placement
Alright, now that we’ve identified those high-value keywords, it’s time to talk about where to place them within your content for maximum SEO impact. Proper keyword placement can make a significant difference in how search engines perceive and rank your content. Here’s how to do it right.

Best Practices for Strategic Keyword Placement
- Title Tag
- Primary Keyword: Always include your primary keyword in the title tag, preferably near the beginning.
- Engagement: Make sure the title is compelling and encourages clicks.
- Length: Keep it under 60 characters to ensure it displays fully in search results.
- Meta Description
- Include Primary Keyword: Naturally incorporate your primary keyword within the first 150-160 characters.
- Engaging and Descriptive: Summarize the content and include a call to action to improve click-through rates.
- Headings (H1, H2, H3, etc.)
- H1 Tag: Use your primary keyword in the H1 tag. This should be the main title of your content.
- Subheadings: Use H2 and H3 tags for subheadings and include secondary keywords to structure the content and improve readability.
- Introduction
- Early Mention: Mention your primary keyword within the first 100 words of your content to signal relevance to search engines.
- Natural Flow: Ensure it fits naturally within the introduction and sets the stage for what the article will cover.
- Body Content
- Primary and Secondary Keywords: Distribute your primary and secondary keywords throughout the content.
- LSI Keywords: Use Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) keywords—related terms that help search engines understand the context of your content.
- Keyword Density: Aim for a keyword density of 1-2%, avoiding overstuffing to prevent penalties.
- URL
- Descriptive and Clean: Include your primary keyword in the URL to give users and search engines a clear idea of what the page is about.
- Short and Simple: Keep URLs concise and avoid unnecessary parameters or numbers.
- Image Optimization
- Alt Text: Describe images with relevant keywords to improve accessibility and help search engines understand the image context.
- File Names: Name your image files descriptively using keywords (e.g., “best-soil-vegetable-gardening.jpg”).
- Captions: If appropriate, use captions with keywords to enhance the relevance.
- Internal Links
- Keyword-Rich Anchor Text: Use descriptive, keyword-rich anchor text for internal links to guide users and distribute page authority.
- Related Content: Link to other relevant content on your site to keep users engaged and improve site navigation.
- External Links
- High-Quality Sources: Link to authoritative sources that support your content, using keywords naturally in the anchor text.
- Relevance: Ensure that the external links are relevant to your content and add value for your readers.
- Conclusion
- Reiterate Keywords: Naturally mention your primary and secondary keywords in the conclusion to reinforce the main points.
- Call to Action: Encourage readers to engage further, whether it’s reading more articles, signing up for a newsletter, or making a purchase.
Example of Strategic Keyword Placement
Let’s put this into practice with an example topic: “Best Soil for Vegetable Gardening.”
- Title Tag: “Best Soil for Vegetable Gardening: Top Picks for Healthy Plants”
- Meta Description: “Discover the best soil for vegetable gardening to ensure healthy, thriving plants. Learn top soil picks and expert gardening tips.”
- H1 Tag: “Best Soil for Vegetable Gardening”
- Introduction: “Choosing the best soil for vegetable gardening is crucial for growing healthy, robust vegetables. In this guide, we’ll explore the top soil options and tips for maintaining fertile soil.”
- Subheadings:
- H2: “Why Soil Quality Matters”
- H2: “Top Soils for Vegetable Gardens”
- H3: “Organic Soil Options”
- H3: “Best Soil for Container Gardening”
- Body Content: Include primary and secondary keywords like “organic soil,” “container gardening soil,” and “vegetable garden soil.”
- URL: “yourwebsite.com/best-soil-vegetable-gardening”
- Image Optimization:
- Alt Text: “Organic soil for vegetable gardening”
- File Name: “organic-soil-vegetable-gardening.jpg”
- Internal Links: Link to related articles like “How to Start a Vegetable Garden” and “Top Vegetables to Grow at Home.”
- Conclusion: “Choosing the best soil for vegetable gardening can make a significant difference in your plant’s health and yield. Explore our recommended soils and start growing your best garden yet. Check out our related articles for more gardening tips.”
Meta Tags: Titles and Descriptions
Meta tags might seem like small pieces of the SEO puzzle, but they play a big role in how your pages are indexed and presented by search engines. Let’s break down the importance of title tags and meta descriptions, and how to optimize them effectively for better rankings and click-through rates (CTR).
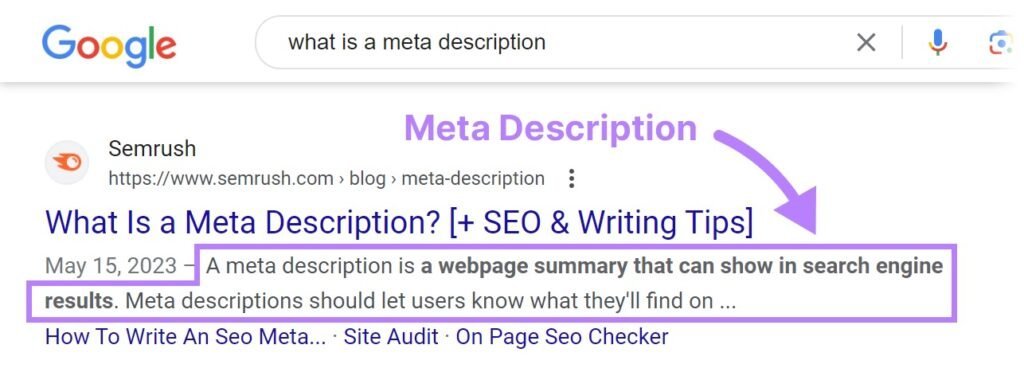
The Role of Meta Tags in SEO
Meta tags provide search engines and users with information about your webpage. While they don’t directly impact search engine rankings, they significantly influence how your page appears in search results and can affect CTR. Higher CTR can lead to better rankings over time as search engines perceive your content as valuable.
Title Tags
What are Title Tags? Title tags are HTML elements that specify the title of a web page. They are displayed on search engine results pages (SERPs) as the clickable headline for a given result and are important for usability, SEO, and social sharing.
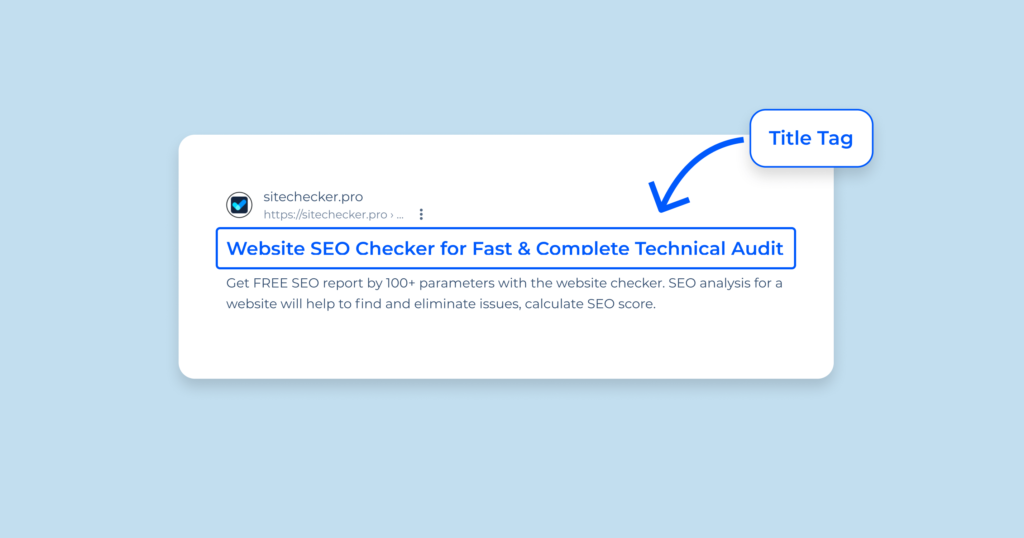
Why are They Important?
- First Impression: Title tags are the first thing users see in SERPs, influencing their decision to click.
- Relevance: Search engines use title tags to understand the content of a page.
- SEO: Properly optimized title tags can improve your page’s search engine ranking.
Best Practices for Optimizing Title Tags
- Include Primary Keyword: Place your primary keyword close to the beginning of the title tag.
- Keep It Under 60 Characters: To ensure it’s fully visible in SERPs.
- Unique Titles for Each Page: Avoid duplicate title tags across your site.
- Engaging and Descriptive: Make your title tags compelling to encourage clicks.
- Branding: If relevant, include your brand name at the end of the title tag.
Example:
- Without Optimization: “Gardening Tips”
- Optimized: “Top 10 Gardening Tips for Beginners | Your Brand”
Meta Descriptions
What are Meta Descriptions? Meta descriptions are HTML attributes that provide brief summaries of web pages. They appear under the title tag in SERPs and influence click-through rates, but they don’t directly affect rankings.
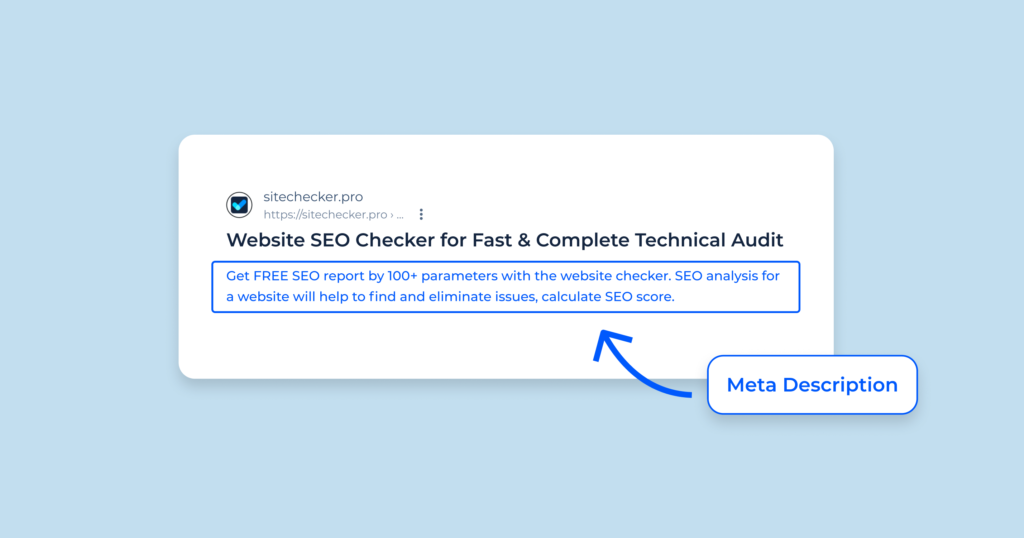
Why are They Important?
- CTR: A well-written meta description can significantly increase your CTR.
- User Experience: Helps users understand what your page is about before clicking.
- Social Sharing: Meta descriptions often appear when your page is shared on social media.
Best Practices for Optimizing Meta Descriptions
- Include Primary Keyword: Naturally incorporate your primary keyword.
- 150-160 Characters: Ensure your description is concise and fully visible in SERPs.
- Unique Descriptions for Each Page: Avoid duplicate meta descriptions.
- Compelling and Clear: Summarize the content accurately and include a call to action.
- Align with Page Content: Ensure your meta description accurately reflects the page’s content to avoid high bounce rates.
Example:
- Without Optimization: “Learn about gardening.”
- Optimized: “Discover the top 10 gardening tips for beginners to grow your green thumb. Get expert advice and start your garden today!”
Practical Tips for Crafting Meta Tags
- Keyword Placement
- Title Tag: “Best Organic Fertilizers for Your Garden | GreenThumb”
- Meta Description: “Find the best organic fertilizers to boost your garden’s health. Explore top-rated products and expert tips for lush, thriving plants.”
- Character Limits
- Title Tag: Keep it under 60 characters to avoid truncation.
- Meta Description: Aim for 150-160 characters to ensure the full description is displayed.
- Unique and Specific
- Title Tag: Avoid generic titles. Instead of “Gardening Tips,” use “10 Essential Gardening Tips for Beginners.”
- Meta Description: Be specific. Instead of “Learn about gardening,” use “Discover essential gardening tips and tricks for beginners to start your own garden successfully.”
- Engagement
- Title Tag: Use words that generate interest and urgency, such as “Top,” “Best,” “Guide,” or “Essential.”
- Meta Description: Include a call to action, like “Learn more,” “Discover now,” or “Get started today.”
Crafting Effective Title Tags
Title tags are a critical component of on-page SEO and play a vital role in influencing both your search engine rankings and click-through rates (CTR). Here’s how to craft title tags that not only rank well but also attract clicks.
Why Title Tags Matter
Title tags are the first impression users get of your webpage in the search engine results pages (SERPs). They inform both search engines and users about the content of your page. A well-crafted title tag can:
- Improve Rankings: Search engines use title tags to understand the relevance of your content.
- Increase CTR: Compelling title tags attract more clicks, driving more traffic to your site.
- Enhance User Experience: Accurate and descriptive titles help users find the content they’re looking for.
Techniques for Crafting Effective Title Tags
- Include Primary Keywords
- Relevance: Place your primary keyword close to the beginning of the title tag.
- Natural Integration: Ensure the keyword fits naturally within the title.
- Keep It Concise
- Character Limit: Aim for 50-60 characters to ensure the entire title is visible in SERPs.
- Avoid Truncation: Longer titles may get cut off, leading to incomplete information.
- Make It Compelling
- Engage the User: Use power words and action phrases that encourage clicks.
- Highlight Benefits: Showcase the value or benefit of clicking on your link.
- Include Branding (When Appropriate)
- Brand Recognition: Adding your brand name can help build brand awareness and trust.
- Positioning: Place your brand name at the end of the title tag to prioritize keywords.
- Use Numbers and Lists
- Clear Expectations: Numbers and lists provide clarity and attract attention.
- Structure: They suggest a well-organized and easy-to-read article.
- Leverage Emotional Triggers
- Curiosity: Pique interest by creating a sense of curiosity or urgency.
- Desire: Use words that evoke a positive emotional response.
- Match User Intent
- Alignment: Ensure your title accurately reflects the content and meets the user’s search intent.
- Avoid Clickbait: Misleading titles can increase bounce rates and harm your rankings.
- Optimize for Multiple Devices
- Mobile-Friendly: Consider how your title will appear on mobile devices. Shorter titles are often better.
- Responsive: Ensure the title is readable and engaging on both desktop and mobile SERPs.
Practical Examples
Let’s take a generic topic and transform it into an effective title tag.
Topic: Benefits of Exercise
- Generic Title: “The Benefits of Exercise”
- Optimized Title: “10 Surprising Benefits of Daily Exercise | FitLife”
- With Emotional Trigger: “Transform Your Health: 10 Surprising Benefits of Daily Exercise”
- Numbered List and Brand: “Top 10 Benefits of Daily Exercise | FitLife”
Topic: Baking a Chocolate Cake
- Generic Title: “How to Bake a Chocolate Cake”
- Optimized Title: “Easy Chocolate Cake Recipe: Step-by-Step Guide”
- With Branding: “Easy Chocolate Cake Recipe: Step-by-Step Guide | SweetTreats”
- Engaging: “Bake the Perfect Chocolate Cake: Easy Recipe & Tips”
Writing Compelling Meta Descriptions
Meta descriptions are your opportunity to convince searchers to click through to your website. Although they don’t directly influence rankings, they play a significant role in improving click-through rates (CTR) and driving traffic. Let’s explore the guidelines for writing meta descriptions that captivate users and enhance your SEO efforts.
Why Meta Descriptions Matter
- First Impression: They provide a snapshot of your page’s content, influencing a user’s decision to click.
- CTR: Well-crafted meta descriptions can significantly increase your CTR.
- User Experience: They set expectations for what users will find on your page.
- Rich Snippets: Properly formatted descriptions can lead to enhanced listings with rich snippets.
Guidelines for Writing Compelling Meta Descriptions
- Keep It Concise
- Optimal Length: Aim for 150-160 characters to ensure the entire description is visible in SERPs.
- Avoid Truncation: Ensure the main message is within the visible character limit.
- Include Primary Keywords
- Relevance: Naturally incorporate your primary keyword to signal relevance to search engines and users.
- Highlight Key Terms: Use bold keywords to catch the user’s eye.
- Be Descriptive and Specific
- Summarize Content: Provide a clear and accurate summary of what the page is about.
- Avoid Vague Descriptions: Ensure users know exactly what to expect.
- Include a Call to Action (CTA)
- Encourage Action: Use action-oriented language to prompt users to click.
- Clear Benefits: Highlight what users will gain by visiting your page.
- Match User Intent
- Alignment: Ensure the meta description aligns with the search intent behind the keyword.
- Relevance: Accurately reflect the content to reduce bounce rates and increase user satisfaction.
- Use Compelling Language
- Engage the Reader: Use persuasive language that draws users in.
- Evoke Curiosity: Pique interest by promising valuable information or solutions.
- Highlight Unique Selling Points (USPs)
- Stand Out: Mention what makes your content unique or superior.
- Value Proposition: Clearly state the benefit or solution provided by your content.
- Format for Readability
- Clarity: Use simple and clear language.
- Avoid Jargon: Ensure it’s understandable to a broad audience.
Practical Examples
Topic: Benefits of Drinking Water
- Without Optimization: “Drinking water is important.”
- Optimized: “Discover the top 10 benefits of drinking water daily. Improve your health, boost energy levels, and enhance skin glow with these tips.”
Topic: Home Office Setup
- Without Optimization: “How to set up a home office.”
- Optimized: “Create the perfect home office with our easy setup guide. From ergonomic furniture to tech essentials, find everything you need to boost productivity.”
Topic: Vegan Recipes
- Without Optimization: “Vegan recipes.”
- Optimized: “Explore our delicious vegan recipes for every meal. Healthy, easy-to-make dishes that even meat-eaters will love. Try them today!”
Content Quality and Relevance
Creating high-quality, relevant content is at the heart of effective SEO. It’s what keeps users engaged, satisfies their needs, and signals to search engines that your site is a valuable resource. Let’s explore how to ensure your content hits the mark every time.
Why Content Quality and Relevance Matter
- User Engagement: Quality content keeps users on your site longer, reducing bounce rates and increasing time spent on the page.
- SEO Rankings: Search engines prioritize content that is valuable, relevant, and authoritative.
- User Intent: Meeting user intent leads to higher satisfaction, better engagement, and more conversions.
- Authority and Trust: High-quality content establishes your site as an authority in your niche, building trust with your audience.
Ensuring High-Quality Content
- Thorough Research
- Accurate Information: Ensure your content is based on reliable sources and up-to-date information.
- Depth: Cover topics comprehensively, addressing various aspects and related subtopics.
- Originality
- Unique Perspective: Offer fresh insights or a unique angle on common topics.
- Avoid Plagiarism: Ensure all content is original and properly cite any references.
- Clear and Engaging Writing
- Readability: Use clear, concise language and short paragraphs to make content easy to read.
- Engagement: Use storytelling, humor, or personal anecdotes to make content more engaging.
- Visuals and Media
- Images and Videos: Include relevant images, infographics, and videos to enhance understanding and break up text.
- Alt Text: Use descriptive alt text for images to improve accessibility and SEO.
- User Experience (UX)
- Navigation: Ensure your site is easy to navigate with clear headings and logical flow.
- Mobile-Friendly: Optimize for mobile devices to ensure a seamless experience across all platforms.
- Updating Content
- Regular Updates: Keep content fresh and relevant by updating it regularly.
- Evergreen Content: Create content that remains relevant over time, with periodic updates to maintain accuracy.
Ensuring Content Relevance
- Understand User Intent
- Types of Intent: Identify whether the user intent is informational, navigational, transactional, or commercial investigation.
- Content Alignment: Align your content with the identified user intent to meet their needs effectively.
- Keyword Optimization
- Primary and Secondary Keywords: Use a mix of primary and secondary keywords naturally throughout the content.
- Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) Keywords: Include related terms and phrases to cover the topic comprehensively.
- Audience Analysis
- Target Audience: Understand the demographics, preferences, and pain points of your target audience.
- Personalization: Tailor your content to address specific interests and needs of your audience segments.
- Answering User Questions
- FAQs: Include frequently asked questions to address common queries related to your topic.
- Comprehensive Coverage: Ensure your content answers the main questions and sub-questions users might have.
- Content Structure
- Headings and Subheadings: Use descriptive headings and subheadings to organize content logically and improve readability.
- Bullet Points and Lists: Use bullet points and lists to break down information into digestible chunks.
- Internal Linking
- Relevant Links: Link to other relevant content on your site to provide additional value and keep users engaged.
- Anchor Text: Use descriptive and keyword-rich anchor text for internal links.
Practical Examples
Topic: Health Benefits of Yoga
- High-Quality Content: Include well-researched benefits, supported by scientific studies, personal anecdotes, and expert quotes.
- Relevance: Address the intent of users looking for health benefits by including sections on physical, mental, and emotional benefits.
- User Engagement: Use engaging language, add images of yoga poses, and include a video tutorial.
Topic: Digital Marketing Strategies
- High-Quality Content: Provide in-depth analysis of different strategies, case studies, and actionable tips.
- Relevance: Target marketers looking to improve their skills with comprehensive guides, examples, and practical advice.
- User Engagement: Use infographics to illustrate strategies and include links to related articles on SEO, social media marketing, and email campaigns.
Creating Valuable Content
Creating valuable content is essential for engaging readers and boosting your SEO. It’s not just about producing text; it’s about delivering information that resonates with your audience, answers their questions, and keeps them coming back for more. Let’s delve into how to create content that’s both valuable and informative.

Why Valuable Content Matters
- User Engagement: High-quality content keeps readers on your site longer, reducing bounce rates.
- SEO Rankings: Search engines favor content that is useful, relevant, and comprehensive.
- Building Trust: Valuable content establishes your site as an authority in your niche, building trust with your audience.
- Social Sharing: Content that provides real value is more likely to be shared, increasing your reach.
Steps to Creating Valuable and Informative Content
- Understand Your Audience
- Identify Needs and Interests: Know who your audience is and what they care about.
- Create Buyer Personas: Develop detailed profiles of your target audience to tailor content specifically for them.
- Conduct Thorough Research
- Reliable Sources: Use credible and authoritative sources to gather information.
- Depth: Cover topics comprehensively to provide thorough answers and insights.
- Offer Unique Insights
- Original Content: Provide a unique perspective or approach to a common topic.
- Personal Experience: Share your own experiences or case studies to add a personal touch.
- Use Engaging and Clear Language
- Readability: Use clear, concise language and avoid jargon unless it’s well-explained.
- Engagement: Write in an engaging tone that resonates with your audience.
- Incorporate Visuals and Media
- Images and Infographics: Use visuals to break up text and illustrate key points.
- Videos: Include video tutorials or explanations for a more dynamic experience.
- Structure Your Content
- Headings and Subheadings: Use descriptive headings to organize content and improve readability.
- Bullet Points and Lists: Break down information into easily digestible chunks.
- Answer User Questions
- Comprehensive Coverage: Address all potential questions and subtopics related to the main topic.
- FAQs: Include a section for frequently asked questions to cover additional queries.
- Internal and External Linking
- Internal Links: Link to related content on your site to provide additional value and keep users engaged.
- External Links: Link to authoritative sources to back up your claims and provide further reading.
- Call to Action (CTA)
- Engage Users: Encourage readers to take action, whether it’s commenting, sharing, or exploring more content.
- Clear and Compelling: Make your CTA clear and motivating.
- Regularly Update Content
- Keep It Fresh: Regularly update your content to ensure it remains accurate and relevant.
- New Insights: Add new information or insights as they become available.
Practical Example
Topic: Healthy Smoothie Recipes
- Audience Understanding: Focus on health-conscious individuals looking for easy, nutritious recipes.
- Thorough Research: Include scientifically-backed health benefits of ingredients.
- Unique Insights: Share personal favorite recipes or unique ingredient combinations.
- Engaging Language: Use an enthusiastic and encouraging tone.
- Visuals: Add high-quality images of each smoothie and a video tutorial.
- Structure: Use headings like “Benefits of Smoothies,” “Essential Ingredients,” and “Top 5 Recipes.”
- Answer Questions: Include FAQs like “What are the best fruits for smoothies?” and “Can I use frozen fruits?”
- Internal and External Links: Link to related articles on healthy eating and external studies on nutrition.
- CTA: “Try these delicious smoothies today and feel the difference! Share your favorite recipe in the comments below.”
- Regular Updates: Periodically update the post with new recipes and trends.
By focusing on these elements, you can create content that is not only informative and engaging but also highly valuable to your audience, driving better SEO results and user satisfaction.
Updating and Refreshing Content
Keeping your content fresh and up-to-date is crucial for maintaining relevance, improving user experience, and sustaining or enhancing search engine rankings. Let’s dive into why updating and refreshing content is important and how to do it effectively.
Why Updating and Refreshing Content Matters
- Maintaining Relevance
- Current Information: Ensures your content reflects the latest information, trends, and developments.
- User Trust: Updated content builds trust with your audience, as they can rely on your site for accurate and timely information.
- SEO Benefits
- Improved Rankings: Search engines favor updated content, potentially boosting your rankings.
- Increased Traffic: Fresh content can attract new visitors and re-engage existing ones.
- Enhanced User Experience
- Useful Content: Providing up-to-date information enhances the value of your content for users.
- Engagement: Users are more likely to engage with and share current, relevant content.
- Fixing Issues
- Outdated Information: Correct outdated or inaccurate information.
- Broken Links: Identify and fix broken links to improve user experience and SEO.
How to Update and Refresh Content Effectively
- Perform a Content Audit
- Identify Outdated Content: Review your site to identify content that needs updating.
- Analyze Performance: Use analytics to determine which pieces of content are underperforming and why.
- Update Information
- Current Data: Replace outdated statistics, facts, and figures with the most recent data.
- New Developments: Incorporate the latest trends, research, and industry developments.
- Improve Content Quality
- Enhance Readability: Break up long paragraphs, add subheadings, and improve the overall structure.
- Add Visuals: Include new images, videos, infographics, or charts to enhance the content.
- Expand and Deepen Content
- Add New Sections: Introduce new sections or subsections to provide more comprehensive coverage of the topic.
- Address New Questions: Include additional FAQs or common questions that have arisen since the original publication.
- Optimize for SEO
- Keywords: Re-evaluate and update keywords to align with current search trends.
- Meta Tags: Refresh title tags and meta descriptions to improve CTR.
- Check and Fix Links
- Internal Links: Ensure all internal links are still relevant and working.
- External Links: Update or replace broken external links with current and authoritative sources.
- Promote Updated Content
- Social Media: Share the refreshed content on your social media channels to drive new traffic.
- Email Newsletters: Notify your subscribers about the updated content through your newsletter.
- Regular Review Schedule
- Consistent Updates: Set a schedule for regular content reviews and updates.
- Priority: Focus on high-traffic and evergreen content that provides the most value to your audience.
Practical Example
Topic: Beginner’s Guide to SEO
- Content Audit: Identify that the guide was last updated two years ago and contains outdated SEO tactics.
- Update Information: Replace old tactics with current best practices, including the latest algorithm updates.
- Improve Quality: Add new sections on mobile SEO and voice search, enhance readability with subheadings and bullet points.
- Expand Content: Include a new FAQ section addressing recent common questions about SEO.
- Optimize for SEO: Update keywords to include current trends like “SEO strategies 2024” and refresh meta tags.
- Check Links: Replace broken links with updated resources from authoritative sources.
- Promote: Share the updated guide on social media and through an email newsletter to drive traffic.
- Regular Review: Schedule a review every six months to ensure the guide remains up-to-date.
Header Tags (H1, H2, H3)
Header tags are essential for structuring your content, improving readability, and boosting your SEO. Properly utilizing header tags (H1, H2, H3) helps both search engines and users understand the hierarchy and key points of your content. Let’s explore how to use header tags effectively.
Why Header Tags Matter
Improved Readability
- Structure: Header tags break up text into manageable sections, making content easier to read.
- User Experience: Clear headings guide readers through your content, enhancing their experience.
SEO Benefits
- Keyword Placement: Strategically placing keywords in header tags can improve search engine rankings.
- Content Hierarchy: Search engines use header tags to understand the structure and importance of content.
Accessibility
- Screen Readers: Header tags help screen readers navigate and understand the content, improving accessibility for visually impaired users.
How to Use Header Tags Effectively
H1 Tag: The Main Title
- Single H1: Each page should have only one H1 tag, which serves as the main title of the content.
- Primary Keyword: Include the primary keyword to signal the main topic of the page.
- Example: Ultimate Guide to Organic Gardening
H2 Tags: Primary Subheadings
- Major Sections: Use H2 tags to denote the primary sections of your content.
- Keywords: Include secondary keywords to enhance SEO.
- Examples:
- Benefits of Organic Gardening
- Getting Started with Organic Gardening
H3 Tags: Subsections
- Subtopics: Use H3 tags for subsections under the H2 headings to further break down content.
- Detailed Points: Include specific points or steps within the primary sections.
- Examples:
- Choosing the Right Soil
- Planting Techniques
Additional Header Tags (H4, H5, H6)
- Further Breakdown: Use H4, H5, and H6 tags if your content requires further subdivision beyond H3 tags.
- Less Frequent: These are less commonly used but can be helpful for very detailed content.
- Examples:
- Soil Preparation Tips
- Composting
Consistency and Hierarchy
- Logical Flow: Ensure a logical and hierarchical flow from H1 to H2, H3, and so on.
- Avoid Skipping Levels: Do not skip header levels (e.g., from H2 directly to H4).
- Example:
- Planning Your Organic Garden
- Selecting Plants
- Designing Garden Layout
- Planning Your Organic Garden
Use Descriptive Headers
- Clarity: Make sure each header clearly describes the section it introduces.
- Relevance: Headers should be relevant to the content and provide a clear indication of what follows.
- Example:
- Top Organic Fertilizers for Vegetables
- Compost
- Worm Castings
- Top Organic Fertilizers for Vegetables
Enhance User Experience
- Skimmable Content: Well-structured headers make it easy for users to skim the content and find what they’re looking for.
- Visual Breaks: Headers create visual breaks, making long content less intimidating.
Optimize for Featured Snippets
- Questions and Answers: Use headers to format content in a way that answers specific questions, which can help capture featured snippets.
- Structured Data: Combine header tags with structured data to improve the chances of being featured in snippets.
- Example:
- How to Start an Organic Garden?
- Step 1: Choose Your Location
- Step 2: Prepare the Soil
- How to Start an Organic Garden?
Practical Example
Topic: Starting a Vegetable Garden
H1 Tag:
- Starting a Vegetable Garden: A Beginner’s Guide
H2 Tags:
- Why Start a Vegetable Garden?
- Choosing the Right Location
- Preparing the Soil
- Planting Your Vegetables
- Maintaining Your Garden
H3 Tags:
- Sunlight Requirements
- Watering Needs
- Soil Types and Preparation
- Planting Techniques
- Weeding and Pest Control
Using H1 Tags Correctly
The H1 tag is a crucial element of on-page SEO. It signals the main topic of the page to search engines and sets the stage for the rest of your content. Here are the best practices for using H1 tags effectively.

Best Practices for Using H1 Tags
One H1 Tag per Page
- Unique Title: Each page should have only one H1 tag to avoid confusion and clearly signal the main topic.
- Clarity: The H1 should give a clear and concise indication of the page’s content.
- Example:
- Ultimate Guide to Organic Gardening
Include Primary Keyword
- Relevance: Incorporate the primary keyword naturally within the H1 tag to improve SEO.
- Avoid Keyword Stuffing: Ensure the keyword fits seamlessly and avoid overstuffing.
- Example:
- Effective SEO Strategies for Small Businesses
Be Descriptive and Specific
- Detail: Make the H1 tag descriptive enough to inform readers about the specific focus of the content.
- Avoid Vagueness: The title should not be too broad or generic.
- Example:
- 10 Essential Tips for Growing Organic Vegetables
Align with Page Content
- Consistency: Ensure that the H1 tag accurately reflects the content of the page.
- Expectation Setting: The title should set the right expectations for what the reader will learn or find on the page.
- Example:
- Step-by-Step Guide to Building a Backyard Greenhouse
Optimize for Users and Search Engines
- Readable: The H1 tag should be easily readable and make sense to both humans and search engines.
- Engaging: Craft the H1 to be engaging and enticing to encourage users to continue reading.
- Example:
- How to Create a Sustainable Home Garden: A Beginner’s Guide
Use Proper Formatting
- HTML Syntax: Use the correct HTML syntax for the H1 tag.
- Styling: Ensure the H1 tag is visually distinct from other headings on the page.
- Example:
- Top 5 Benefits of Daily Exercise
Avoid Duplicate H1 Tags
- Unique Content: Each page on your site should have a unique H1 tag to avoid duplication.
- Distinct Topics: Differentiate the H1 tags on each page to reflect the unique content and focus of each page.
- Example:
- How to Start a Vegetable Garden in Small Spaces
- Choosing the Best Vegetables for Your Small Garden
Maintain a Clear Hierarchy
- Page Structure: Use the H1 tag as the primary heading, followed by H2, H3, and other subheadings to create a clear hierarchy.
- Logical Flow: Ensure the content flows logically from the H1 tag to subheadings and body content.
- Example:
- Complete Guide to Organic Gardening
- Introduction to Organic Gardening
- Benefits of Organic Gardening
Contextual Relevance
- Topical Consistency: Ensure the H1 tag is contextually relevant to the rest of the page content.
- Thematic Focus: Maintain a thematic focus that aligns with the H1 tag.
- Example:
- Effective Content Marketing Strategies for 2024
Practical Example
Topic: Benefits of Yoga
- One H1 Tag: Top 10 Health Benefits of Practicing Yoga
- Include Primary Keyword: Top 10 Health Benefits of Practicing Yoga Daily
- Descriptive and Specific: 10 Surprising Health Benefits of Daily Yoga Practice
- Align with Content: Comprehensive Guide to the Health Benefits of Yoga
- Readable and Engaging: Discover the Amazing Health Benefits of Yoga
Organizing Content with H2 and H3 Tags
Using H2 and H3 tags effectively is crucial for organizing your content into logical sections, enhancing readability, and improving SEO. These tags help break down your content into manageable parts, making it easier for readers and search engines to understand the structure and flow. Here’s how to use H2 and H3 tags to your advantage.

Importance of H2 and H3 Tags
- Readability: Helps readers quickly scan and find the information they need.
- SEO: Search engines use these tags to understand the hierarchy and relevance of the content.
- User Experience: Improves overall user experience by structuring content logically.
Best Practices for Using H2 Tags
Primary Sections
- Major Points: Use H2 tags to denote the main sections or topics of your content.
- Keyword Usage: Include secondary keywords where appropriate to enhance SEO.
- Example:
- Benefits of Organic Gardening
- Getting Started with Organic Gardening
Clear and Descriptive
- Informative: Ensure each H2 tag clearly describes the section it introduces.
- Engaging: Use compelling language to keep readers interested.
- Example:
- Top Health Benefits of Daily Exercise
- How to Create a Sustainable Home Garden
Consistent Formatting
- Uniformity: Maintain consistent formatting and style for all H2 tags.
- Hierarchy: Ensure H2 tags follow the H1 tag logically.
- Example:
- Complete Guide to Organic Gardening
- Introduction to Organic Gardening
- Choosing the Right Plants
Logical Flow
- Sequential Order: Organize H2 tags in a logical sequence that guides the reader through the content.
- Coherence: Each H2 tag should introduce a section that naturally follows the previous one.
- Example:
- Planning Your Organic Garden
- Preparing the Soil
- Planting Techniques
Best Practices for Using H3 Tags
Subsections of H2 Tags
- Detailed Points: Use H3 tags to break down the main sections (H2) into more detailed points.
- Specific Topics: Focus on specific aspects of the H2 section.
- Example:
- Preparing the Soil
- Testing Soil pH
- Amending the Soil
- Preparing the Soil
Keyword Optimization
- Relevant Keywords: Include relevant keywords to enhance SEO without overstuffing.
- Natural Integration: Ensure keywords fit naturally within the H3 tags.
- Example:
- Health Benefits of Yoga
- Physical Benefits
- Mental Benefits
- Health Benefits of Yoga
Enhance Readability
- Concise and Clear: Make H3 tags concise and clear to improve readability.
- Subdividing Content: Use H3 tags to divide content into easily digestible parts.
- Example:
- Organic Pest Control Methods
- Natural Pesticides
- Companion Planting
- Organic Pest Control Methods
Maintain Consistency
- Uniform Style: Keep the style and formatting of H3 tags consistent throughout the content.
- Logical Progression: Ensure H3 tags logically follow the H2 tags and maintain a clear hierarchy.
- Example:
- Benefits of Daily Exercise
- Improves Cardiovascular Health
- Boosts Mental Health
- Benefits of Daily Exercise
Practical Examples
Topic: Starting a Vegetable Garden
H1 Tag:
- Starting a Vegetable Garden: A Beginner’s Guide
H2 Tags:
- Planning Your Vegetable Garden
- Preparing the Soil
- Planting Your Vegetables
- Maintaining Your Garden
H3 Tags:
Planning Your Vegetable Garden
- Choosing the Right Location
- Selecting Your Vegetables
Preparing the Soil
- Testing Soil Quality
- Adding Organic Matter
Planting Your Vegetables
- Sowing Seeds
- Transplanting Seedlings
Maintaining Your Garden
- Watering Techniques
- Pest Control Methods
By using H2 and H3 tags effectively, you can create a well-organized, easy-to-read structure that enhances both user experience and SEO. Properly structured content helps readers find the information they need quickly and signals to search engines the importance and relevance of your content.
Internal Linking
A robust internal linking strategy is essential for improving site navigation, distributing link equity, and enhancing user experience. By strategically linking pages within your website, you help search engines understand the structure of your site and guide users to valuable content. Here’s how to develop an effective internal linking strategy.
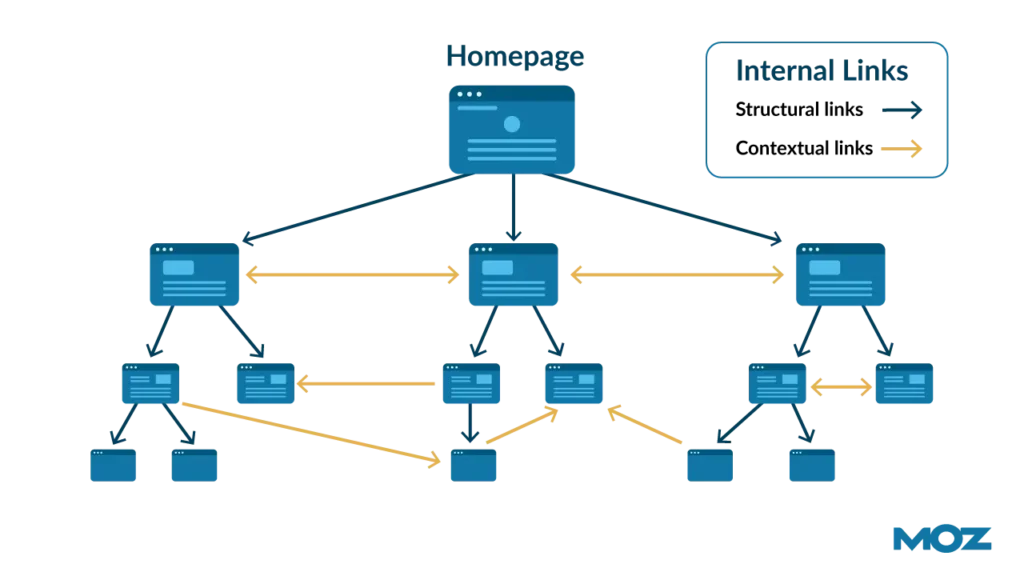
Why Internal Linking Matters
- Improved Navigation: Helps users find related content, enhancing their experience and keeping them on your site longer.
- Link Equity Distribution: Spreads link equity throughout your site, boosting the authority of individual pages.
- SEO Benefits: Helps search engines understand the structure of your site and index your pages more effectively.
- Lower Bounce Rates: Encourages users to explore more pages, reducing bounce rates.
Best Practices for Internal Linking
Use Descriptive Anchor Text
- Relevance: Use clear, descriptive anchor text that indicates what the linked page is about.
- Keywords: Incorporate relevant keywords naturally within the anchor text.
- Example: For a comprehensive guide on organic gardening tips, check out our organic gardening tips.
Link to Relevant Content
- Contextual Relevance: Ensure the linked content is relevant to the context of the current page.
- Value Addition: Link to pages that add value or provide additional information on the topic.
- Example: In our guide on starting a vegetable garden, you’ll find detailed steps for beginners.
Create Deep Links
- Depth: Link to deeper pages within your site, not just the homepage or top-level pages.
- Content Depth: Encourage exploration of specific, detailed content.
- Example: Discover the benefits of composting and how it can improve soil health.
Use a Logical Structure
- Hierarchical Structure: Organize your links in a way that reflects the hierarchy of your site.
- User Pathways: Create clear pathways for users to follow, guiding them through related content.
- Example:
- Planning Your Soil
- Learn how to test soil pH before planting.
- Planning Your Soil
Maintain a Reasonable Number of Links
- Avoid Overlinking: Too many links can be overwhelming and diminish their value.
- Quality Over Quantity: Focus on quality, relevant links rather than excessive linking.
- Example: In our ultimate gardening guide, you’ll find resources on soil preparation, planting techniques, and pest control.
Regularly Update Links
- Check for Broken Links: Regularly audit your site to ensure all internal links are working.
- Update Content: Update links to point to the most current and relevant content.
- Example: Make sure to visit our updated guide on latest SEO strategies.
Use Sitemaps
- HTML Sitemap: Create an HTML sitemap to help users find important pages on your site.
- XML Sitemap: Submit an XML sitemap to search engines to ensure all pages are indexed.
Practical Examples
Topic: Starting a Vegetable Garden
- Descriptive Anchor Text: For a detailed step-by-step process, check out our guide on starting a vegetable garden.
- Link to Relevant Content: Once you’ve chosen your vegetables, you’ll need to know the best planting tips to ensure a successful harvest.
- Create Deep Links: Understanding soil nutrients is crucial for a healthy garden.
- Logical Structure:
- Planning Your Garden Layout
- Consider using raised beds for better soil management. Learn more about raised bed gardening.
- Planning Your Garden Layout
- Maintain Reasonable Links: Check out our articles on composting and organic fertilizers for more gardening tips.
- Regularly Update Links: For the latest techniques, visit our updated guide on modern gardening techniques.
By developing a robust internal linking strategy, you can enhance site navigation, distribute link equity effectively, and improve both user experience and SEO performance. Proper internal linking not only helps search engines crawl your site more efficiently but also keeps users engaged and guides them to valuable content.
Linking to Related Content
Linking to related content within your site is a powerful way to enhance SEO and improve user experience. It helps keep visitors engaged by providing additional value and context, and it aids search engines in understanding the structure and relevance of your content. Here are some effective techniques for linking to related content.
Benefits of Linking to Related Content
- Improved User Engagement: Encourages visitors to explore more of your site, reducing bounce rates and increasing time on site.
- SEO Boost: Helps distribute link equity and signals to search engines the importance and relevance of your pages.
- Enhanced User Experience: Provides users with additional resources and information, making their visit more informative and satisfying.
Techniques for Linking to Related Content
Contextual Links
- Natural Integration: Embed links within the body of your content where they fit naturally.
- Relevance: Ensure the linked content is directly related to the topic at hand.
- Example: When planning your garden, it’s essential to consider soil preparation tips to ensure healthy plant growth.
Related Articles Section
- At the End of Articles: Place a “Related Articles” section at the end of your posts to suggest further reading.
- Automated Plugins: Use CMS plugins to automatically generate related posts based on categories or tags.
- Example:
In-Content Callouts
- Highlight Key Resources: Use callout boxes within your content to highlight and link to related articles or guides.
- Visual Appeal: Make them visually distinct to catch the reader’s eye.
- Example:
- Don’t Miss: For a detailed guide on creating nutrient-rich compost, check out our article on composting guide.
Navigation Menus
- Drop-Down Menus: Include links to related content in drop-down menus within your site’s navigation.
- Sidebar Menus: Use sidebar menus to feature links to related categories or recent posts.
- Example:
- Related Topics
Internal Linking Widgets
- Automated Tools: Use widgets or plugins that automatically link to related content based on keywords or tags.
- Dynamic Updates: Ensure the links update dynamically as new content is added to the site.
- Example:
Breadcrumb Navigation
- Path Navigation: Use breadcrumb trails to show the path of pages leading to the current page, linking each step.
- Contextual Positioning: Place breadcrumbs at the top of the page to help users navigate back to related sections.
- Example:
- Home > Gardening > Vegetable Gardening > Starting a Vegetable Garden
Practical Example
Topic: Starting a Vegetable Garden
- Contextual Links: Before planting, make sure to understand the importance of soil nutrients for healthy vegetable growth.
- Related Articles Section:
- In-Content Callouts:
- Related Resource: Want to learn more about soil preparation? Check out our comprehensive soil preparation guide.
- Navigation Menus:
- Related Topics
By implementing these techniques for linking to related content, you can create a more engaging and user-friendly site that encourages visitors to explore further and improves your overall SEO performance. Properly linking related content helps users find valuable information and signals to search engines the connected nature of your content.
Creating a Logical Link Hierarchy
A logical link hierarchy is essential for prioritizing important pages on your website and effectively distributing link authority. By organizing your internal links in a hierarchical manner, you help search engines understand the importance and relevance of each page, which can boost your overall SEO performance. Here’s how to create a logical link hierarchy.
Importance of a Logical Link Hierarchy
- Prioritization: Helps prioritize important pages, ensuring they receive the most link equity.
- SEO: Assists search engines in understanding the structure and importance of your content.
- User Experience: Guides users through your site in a logical and intuitive manner.
Steps to Create a Logical Link Hierarchy
Identify Key Pages
- Core Pages: Determine the most important pages on your site, such as the homepage, category pages, and cornerstone content.
- Supportive Pages: Identify pages that support the core pages, such as blog posts, product pages, and subcategories.
- Example: Home > Gardening > Vegetable Gardening > Organic Gardening Tips
Use a Clear Hierarchical Structure
- Top-Level Pages: Start with your homepage and main category pages.
- Subcategories: Break down categories into subcategories for more specific topics.
- Individual Pages: Link to individual posts, articles, or products under the appropriate subcategories.
- Example:
- Home
- Gardening
- Vegetable Gardening
- Organic Gardening Tips
- Flower Gardening
- Vegetable Gardening
- Gardening Tools
- Gardening
- Home
Link Depth
- Shallow Hierarchy: Avoid deep hierarchies; try to keep important pages within three clicks from the homepage.
- Accessibility: Ensure that users and search engines can easily access all important pages.
- Example: Home > Gardening > Organic Gardening > Organic Fertilizers
Breadcrumb Navigation
- Path Navigation: Use breadcrumb navigation to show the path of pages leading to the current page, linking each step.
- Contextual Positioning: Place breadcrumbs at the top of the page to help users navigate back to related sections.
- Example:
- Home > Gardening > Vegetable Gardening > Organic Gardening Tips
Internal Link Clustering
- Cluster Related Content: Group related content together and link them contextually within articles.
- Supportive Linking: Ensure supportive pages link back to core pages to boost their authority.
- Example: For more on improving soil health, check out our Soil Nutrients Guide and Composting Basics.
Use Sitemaps
- HTML Sitemap: Create an HTML sitemap to help users find important pages on your site.
- XML Sitemap: Submit an XML sitemap to search engines to ensure all pages are indexed.
- Example:
- Home
- Gardening
- Tools
- About Us
- Contact
- Home
Monitor and Adjust
- Analytics: Use web analytics to monitor user behavior and adjust your internal linking strategy accordingly.
- Regular Audits: Perform regular site audits to check for broken links and ensure your hierarchy remains effective.
- Example: Use Google Analytics to track page views and user flow, adjusting links to optimize traffic flow to key pages.
Practical Example
Topic: Gardening Website
Home Page
- Home
Main Categories
- Gardening
- Gardening Tools
- Blog
Subcategories and Articles
- Gardening
- Vegetable Gardening
- Organic Gardening Tips
- Composting Basics
- Flower Gardening
- Vegetable Gardening
- Gardening Tools
- Blog
By creating a logical link hierarchy, you can ensure that important pages on your website receive the attention and authority they deserve, while also providing a clear and intuitive navigation path for your users. This approach not only improves user experience but also helps search engines better understand and rank your content.
Image Optimization
Optimizing images is crucial for improving site speed, enhancing SEO, and providing a better user experience. Here are effective techniques for optimizing images on your website.

Using Descriptive Alt Text
Importance of Descriptive Alt Text
- Accessibility: Descriptive alt text helps visually impaired users understand the content of images through screen readers.
- SEO: Search engines use alt text to understand the context and relevance of images, which can improve your site’s SEO.
- User Experience: Alt text provides context if an image fails to load, ensuring users still get the essential information.
Best Practices for Writing Alt Text
- Be Descriptive: Clearly describe what the image depicts.
- Include Keywords: Naturally incorporate relevant keywords without keyword stuffing.
- Keep it Concise: Be concise but informative; aim for 125 characters or less.
- Avoid Redundancy: Don’t start with “image of” or “picture of” as it’s already implied.
Example:
- Image: A picture of a vegetable garden with various vegetables.
- Alt Text: “Vegetable garden with tomatoes, carrots, and lettuce growing in neat rows.”
Reducing Image File Sizes
Methods for Reducing Image File Sizes
- Choose the Right Format: Use JPEG for photographs, PNG for images with transparency, and SVG for vector graphics.
- Compress Images: Use tools like TinyPNG, JPEG Optimizer, or online compressors to reduce file sizes without significant loss of quality.
- Resize Images: Ensure images are not larger than they need to be. Scale down images to the exact dimensions required on your website.
- Use Modern Formats: Consider using modern image formats like WebP, which provide better compression and quality.
- Enable Lazy Loading: Implement lazy loading to defer the loading of images until they are in the viewport, improving initial load times.
Tools for Image Compression
- TinyPNG: Compresses PNG and JPEG images while preserving quality.
- JPEG Optimizer: Allows for online JPEG compression with quality control.
- ImageOptim: An app that reduces file sizes of images without losing quality for Mac users.
Example:
- Original Image: JPEG photo of a garden, 2MB.
- Optimized Image: Compressed to 300KB using TinyPNG without noticeable quality loss.
Practical Steps to Implement Image Optimization
- Audit Existing Images: Identify all images on your website and assess their current file sizes and alt text.
- Optimize File Sizes: Use compression tools to reduce file sizes and resize images to their required dimensions.
- Add Descriptive Alt Text: Ensure all images have descriptive, concise alt text with relevant keywords.
- Implement Lazy Loading: Use lazy loading to defer the loading of off-screen images.
- Regularly Review: Regularly review new images added to the site to ensure they meet optimization standards.
By optimizing your images, you can significantly enhance your site’s performance, boost your SEO, and provide a superior user experience. Proper image optimization involves a balance of reducing file sizes and using descriptive alt text to ensure accessibility and relevance.
URL Structure
Creating clean and SEO-friendly URL structures is vital for improving indexing, readability, and rankings. Here’s how to craft effective URLs that boost your site’s performance.
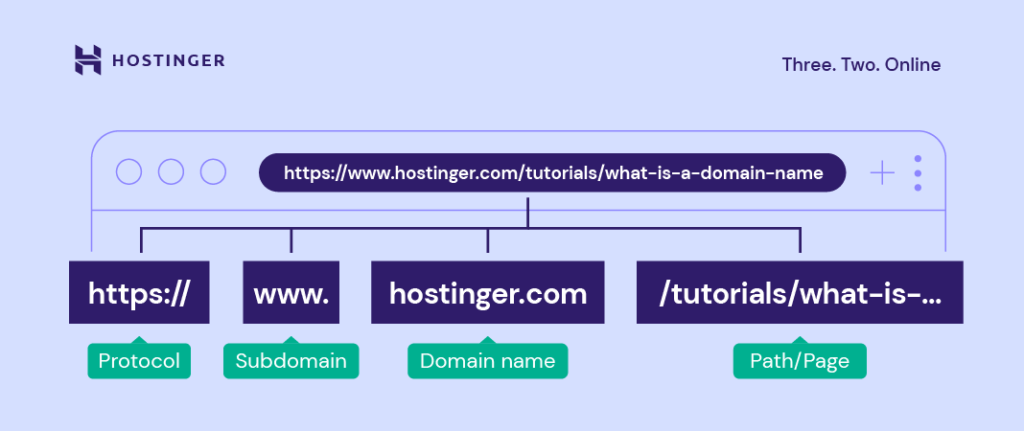
Crafting Descriptive URLs
Tips for Crafting Descriptive and Keyword-Rich URLs
- Use Keywords: Include primary keywords relevant to the page content. This helps search engines understand the topic and improves rankings.
- Be Descriptive: Ensure the URL clearly describes the content of the page. This makes it more user-friendly and helps with SEO.
- Keep it Simple: Shorter URLs are easier to read and remember. Aim for clarity and brevity.
- Use Hyphens, Not Underscores: Separate words with hyphens (e.g., my-site.com/organic-gardening-tips) to improve readability. Search engines treat hyphens as spaces.
- Avoid Stop Words: Words like “and,” “or,” “but,” etc., are often unnecessary in URLs. Removing them can make URLs cleaner and more focused.
Example:
- Good URL: mysite.com/organic-gardening-tips
- Bad URL: mysite.com/page?id=12345
Avoiding Unnecessary Parameters
Importance of Avoiding Unnecessary URL Parameters
- Simplicity: Simple URLs are easier for users to understand and remember.
- SEO Performance: Clean URLs are more attractive to search engines, making indexing more efficient.
- Reduced Risk of Duplicate Content: Parameters can create duplicate content issues, confusing search engines and diluting ranking signals.
Best Practices for Maintaining Simplicity
- Static URLs: Prefer static URLs over dynamic ones with parameters. Static URLs are cleaner and more user-friendly.
- Canonical Tags: Use canonical tags to indicate the preferred URL when parameters are necessary, helping to prevent duplicate content issues.
- URL Rewriting: Use URL rewriting to convert dynamic URLs into static ones. For example, transform “mysite.com/index.php?id=123” into “mysite.com/organic-gardening-tips.”
Example:
- Avoid: mysite.com/index.php?category=gardening&article=organic-tips
- Prefer: mysite.com/gardening/organic-tips
Practical Steps for Implementing SEO-Friendly URLs
- Keyword Research: Identify primary keywords for each page and incorporate them into the URL.
- Simplify Existing URLs: Review current URLs and simplify them by removing unnecessary parameters and words.
- Use Consistent Structure: Develop a consistent URL structure across your site for categories and subcategories.
- Monitor and Update: Regularly review URLs and update them as needed to maintain simplicity and relevance.
Examples of Good URL Practices
Topic: Organic Gardening Tips
- Homepage: mysite.com
- Category Page: mysite.com/gardening
- Subcategory Page: mysite.com/gardening/organic
- Article Page: mysite.com/gardening/organic/composting-tips
By crafting descriptive, keyword-rich URLs and avoiding unnecessary parameters, you can create a URL structure that enhances SEO, improves user experience, and ensures efficient indexing by search engines. Clean URLs are not only easier for search engines to process but also provide a clearer, more intuitive navigation path for users.
Mobile-Friendliness
Ensuring your website is mobile-friendly is crucial for improving user experience and SEO rankings. Here are key strategies to make your site mobile-friendly.

Responsive Design
Importance of Using Responsive Design
- User Experience: A responsive design ensures your website looks great and functions well on all devices, including smartphones, tablets, and desktops. This improves user satisfaction and engagement.
- SEO Benefits: Search engines, especially Google, prioritize mobile-friendly websites in their rankings. Responsive design can boost your SEO performance.
- Cost-Effective: Instead of maintaining separate websites for desktop and mobile, responsive design offers a single site that adapts to any screen size.
Best Practices for Responsive Design
- Flexible Layouts: Use flexible grid layouts that adjust to different screen sizes. This allows your content to flow naturally on various devices.
- Fluid Images: Ensure images resize appropriately across different devices. Use CSS to set images to scale within their containers.
- Media Queries: Utilize CSS media queries to apply different styles based on the device’s screen size. This helps in optimizing the layout for specific devices.
- Touch-Friendly Elements: Design buttons, links, and interactive elements to be easily tappable on touchscreens. Make sure they are large enough and have adequate spacing.
- Viewport Meta Tag: Include the viewport meta tag in your HTML to control the layout on mobile browsers. This ensures the site scales correctly to different screen sizes.
Mobile Page Speed
Techniques for Optimizing Mobile Page Speed
- Optimize Images: Compress images and use next-gen formats to reduce load times without compromising quality.
- Minify CSS and JavaScript: Remove unnecessary characters, spaces, and comments from CSS and JavaScript files to reduce their size.
- Enable Browser Caching: Use browser caching to store static files locally on users’ devices, reducing load times for repeat visits.
- Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN): Distribute your content across multiple servers worldwide to ensure faster load times for users regardless of their location.
- Reduce Server Response Time: Optimize your server settings and use faster hosting solutions to reduce the time it takes for your server to respond to requests.
- Lazy Loading: Implement lazy loading for images and videos to load only when they are visible on the screen, improving initial load times.
- Prioritize Above-the-Fold Content: Ensure the content that appears first on the screen loads quickly, giving the impression of a faster-loading site.
Practical Steps to Ensure Mobile-Friendliness
- Test Your Website: Use tools like Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test and PageSpeed Insights to identify issues and areas for improvement.
- Implement Responsive Design: Ensure your site adapts to different screen sizes and provides a seamless experience across devices.
- Optimize for Speed: Focus on techniques to improve mobile page speed, ensuring fast load times and smooth performance.
- Regular Audits: Regularly check and update your site to maintain mobile-friendliness as technology and best practices evolve.
Examples of Good Mobile-Friendliness Practices
Topic: Gardening Website
- Responsive Layout: Ensure the layout adjusts for different devices, with flexible grids and touch-friendly navigation.
- Optimized Images: Use compressed and properly sized images to enhance load times.
- Fast Load Times: Implement browser caching, lazy loading, and a CDN to ensure quick load times.
- Test Regularly: Use mobile-friendly testing tools to regularly check your site’s performance and usability on mobile devices.
By ensuring your website is mobile-friendly through responsive design and optimized page speed, you can significantly enhance user experience and improve your SEO rankings. A mobile-friendly website is not only a necessity for user satisfaction but also a critical factor in achieving higher visibility in search engine results.
Page Load Speed
Improving page load speed is essential for enhancing user experience and boosting SEO rankings. Here are key strategies to achieve faster page load times.

Reducing Server Response Time
Methods for Reducing Server Response Time
- Optimize Server Configuration: Ensure your server is configured correctly for performance. This includes optimizing database queries and using efficient server-side scripts.
- Upgrade Hosting Plan: Consider upgrading to a better hosting plan or switching to a faster web host. Dedicated or managed hosting can significantly reduce server response times compared to shared hosting.
- Use Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): CDNs distribute your content across multiple servers worldwide, reducing the distance data must travel to reach the user, thus speeding up load times.
- Minimize HTTP Requests: Reduce the number of requests by combining files, using CSS sprites, and minimizing the use of third-party scripts.
- Implement Gzip Compression: Enable Gzip compression to reduce the size of your files before they are sent to the user’s browser, speeding up the transfer.
Leveraging Browser Caching
How Leveraging Browser Caching Can Improve Page Load Speed and SEO
- Store Static Resources Locally: Browser caching stores static files (like images, CSS, and JavaScript) on the user’s device, so they don’t need to be downloaded again on subsequent visits.
- Set Cache Expiry Dates: Specify how long browsers should keep these files before checking for an updated version. This can be set using the HTTP headers.
- Use Long Expiry Times for Unchanged Content: For resources that don’t change often, set a long expiry time to maximize the benefits of caching.
- Optimize Cache-Control Headers: Use Cache-Control headers to define caching policies for both the browser and intermediary caches. This helps in controlling how, and for how long, the content is stored and reused.
- Implement Version Control for Files: Use version control (e.g., appending version numbers to file names) so when you update a file, browsers know to fetch the new version.
Practical Steps to Improve Page Load Speed
- Audit Current Speed: Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, GTmetrix, or Pingdom to analyze your current page load speed and identify areas for improvement.
- Optimize Images and Files: Compress and resize images, minify CSS and JavaScript files, and remove unnecessary code.
- Enhance Server Performance: Upgrade your hosting plan, optimize your server settings, and use CDNs to distribute your content efficiently.
- Implement Browser Caching: Configure your server to leverage browser caching effectively by setting appropriate expiry dates and Cache-Control headers.
- Monitor Regularly: Continuously monitor your site’s performance and make adjustments as needed to maintain optimal speed.
Examples of Good Page Load Speed Practices
Topic: Gardening Website
- Server Optimization: Use a fast hosting provider and a CDN to ensure quick delivery of your gardening content worldwide.
- Efficient File Management: Compress images of garden layouts and plant guides, and minify CSS and JavaScript files.
- Browser Caching: Set long expiry dates for static files like garden images and style sheets, so returning users experience faster load times.
- Regular Speed Audits: Regularly check page load speeds using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights and make necessary adjustments to maintain high performance.
By focusing on reducing server response time and leveraging browser caching, you can significantly improve your website’s page load speed. This not only enhances user experience but also boosts your SEO rankings, making your site more attractive to both visitors and search engines.
Common On-Page SEO Mistakes to Avoid
On-page SEO is crucial for improving your website’s visibility and ranking in search engine results. However, there are common mistakes that can hinder your efforts. Here’s a list of these mistakes and how to avoid them for better rankings.

Keyword Stuffing
Keyword stuffing is an outdated and unethical SEO practice that involves overloading a webpage with keywords or numbers in an attempt to manipulate a site’s ranking in Google’s search results. This practice often leads to a poor user experience and can result in penalties from search engines.
What is Keyword Stuffing?
Keyword stuffing is the practice of inserting an excessive number of keywords into web content, meta tags, or backlinks, often in an unnatural way. This can involve:
- Repeating the same keywords or phrases multiple times within the text.
- Listing keywords or numbers in a group or out of context.
- Using hidden text or links (e.g., white text on a white background) to incorporate keywords invisibly.
Why Keyword Stuffing Should Be Avoided
- Poor User Experience
- Readability: Content that is overloaded with keywords often reads awkwardly and can be difficult for users to understand.
- Engagement: Visitors are likely to leave the site quickly if the content is not useful or engaging, leading to high bounce rates.
- Search Engine Penalties
- Algorithm Updates: Search engines like Google continuously update their algorithms to detect and penalize keyword stuffing.
- Ranking Drops: Sites caught keyword stuffing can experience significant drops in search rankings or be removed from search engine results entirely.
- Damaged Reputation
- Trust Issues: Users may perceive sites that engage in keyword stuffing as untrustworthy or spammy.
- Brand Image: A poor user experience can damage the reputation and credibility of your brand.
- Ineffective SEO Strategy
- Quality Over Quantity: Modern SEO prioritizes high-quality, relevant content over keyword frequency.
- User Intent: Search engines focus on understanding user intent and providing valuable content, not just matching keywords.
Examples of Keyword Stuffing
Visible Keyword Stuffing
- Repeating the same word or phrase excessively within the content.
- Example: “Buy cheap shoes online. Our online store offers the best prices for cheap shoes. Check out our cheap shoes today.”
Hidden Keyword Stuffing
- Using white text on a white background or placing keywords in non-visible areas.
- Example: Inserting a long list of keywords at the bottom of a page in very small or invisible text.
Meta Tag Keyword Stuffing
- Overloading meta tags with keywords in an attempt to manipulate rankings.
- Example:
<meta name="keywords" content="cheap shoes, buy shoes, shoes online, discount shoes, shoes sale, cheap shoes online, best shoes deals">
- Example:
How to Avoid Keyword Stuffing
- Focus on Quality Content
- User-Centric: Write content with the user in mind, ensuring it is valuable, informative, and engaging.
- Natural Language: Use keywords naturally and contextually within the content.
- Use Synonyms and Related Terms
- LSI Keywords: Incorporate Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) keywords, which are related terms and phrases that help search engines understand the context of your content.
- Variety: Use a variety of terms and phrases to avoid repetition and provide a more comprehensive understanding of the topic.
- Optimize Keyword Placement
- Strategic Placement: Place keywords in strategic locations such as the title, headings, meta descriptions, and the first 100 words of the content.
- Avoid Overuse: Ensure that keywords are used in moderation and fit naturally within the content.
- Create Comprehensive Content
- In-Depth Information: Provide thorough, well-researched content that covers the topic comprehensively.
- User Intent: Focus on satisfying the user’s search intent by answering their questions and providing valuable information.
- Regularly Update Content
- Freshness: Keep content up to date with the latest information and best practices.
- Relevance: Regularly review and revise content to ensure it remains relevant and useful to your audience.
Keyword stuffing is a detrimental practice that can harm your website’s rankings, user experience, and reputation. By focusing on creating high-quality, user-centric content and using keywords naturally and strategically, you can improve your SEO performance and provide a better experience for your visitors. Remember, the goal of SEO is to help users find the information they need, not to manipulate search engine rankings through excessive keyword use.
Ignoring Meta Descriptions
Meta descriptions play a significant role in SEO performance and user experience. Ignoring meta descriptions can negatively impact your site’s visibility, click-through rates, and overall search engine rankings. Here’s why meta descriptions are important and the consequences of neglecting them.
Importance of Meta Descriptions
- Improved Click-Through Rates (CTR)
- Attractive Snippets: Meta descriptions appear in search engine results pages (SERPs) beneath the page title and URL, providing a summary of the content. Well-written meta descriptions can attract more clicks.
- Increased Visibility: A compelling meta description can differentiate your listing from others and entice users to click through to your site.
- Enhanced User Experience
- Relevance: Meta descriptions help users understand what the page is about before they click, ensuring that the content meets their needs.
- Expectation Setting: Clear and accurate meta descriptions set the right expectations, reducing bounce rates.
- SEO Benefits
- Keyword Relevance: Including relevant keywords in meta descriptions can improve the relevance of your page to search queries, indirectly influencing rankings.
- Rich Snippets: Meta descriptions can be used to create rich snippets, which enhance the appearance of your listing in SERPs and can improve CTR.
Impact of Ignoring Meta Descriptions
- Missed SEO Opportunities
- Automatic Generation: If you don’t provide a meta description, search engines will automatically generate one from the page content, which may not be as relevant or compelling.
- Less Control: Ignoring meta descriptions means you have less control over how your page appears in SERPs, potentially leading to lower click-through rates.
- Reduced Click-Through Rates (CTR)
- Unattractive Snippets: Automatically generated meta descriptions might not be as attractive or informative, leading to fewer clicks.
- Competitive Disadvantage: Competitors with well-crafted meta descriptions can attract more clicks, even if your page ranks higher.
- Poor User Experience
- Irrelevant Summaries: Automatically generated descriptions might not accurately reflect the page content, leading to a mismatch between user expectations and the actual content.
- Higher Bounce Rates: Users who do click through may quickly leave if the content doesn’t match the description, increasing bounce rates.
- Loss of SERP Real Estate
- No Rich Snippets: Ignoring meta descriptions means missing out on the opportunity to create rich snippets, which can make your listing stand out more in SERPs.
How to Optimize Meta Descriptions
- Write Unique Descriptions for Each Page
- Avoid Duplicates: Ensure each page has a unique meta description that accurately reflects its content.
- Relevance: Tailor descriptions to the specific content and keywords of each page.
- Include Relevant Keywords
- Keyword Placement: Naturally include primary keywords in the meta description to improve relevance.
- Avoid Keyword Stuffing: Use keywords contextually and avoid overloading the description with keywords.
- Focus on User Intent
- Informative and Compelling: Write meta descriptions that inform users about the content and entice them to click.
- Call to Action: Include a call to action (e.g., “Learn more,” “Discover,” “Find out”) to encourage clicks.
- Keep it Concise
- Optimal Length: Aim for a length of 150-160 characters to ensure the entire description is displayed in SERPs.
- Clear and Direct: Be concise and get to the point quickly, providing the essential information users need.
- Test and Iterate
- A/B Testing: Experiment with different meta descriptions to see which versions generate higher CTRs.
- Regular Updates: Periodically review and update meta descriptions to ensure they remain relevant and effective.
Practical Examples
Effective Meta Description for a Blog Post
- Page Title: “10 Tips for Organic Gardening”
- Meta Description: “Learn how to grow a thriving organic garden with our top 10 expert tips. Discover the best practices for soil preparation, pest control, and more. Start your organic gardening journey today!”
Effective Meta Description for a Product Page
- Page Title: “Eco-Friendly Water Bottles”
- Meta Description: “Shop our range of eco-friendly water bottles made from sustainable materials. Stay hydrated while reducing your environmental impact. Free shipping on orders over $50. Order now!”
By optimizing your meta descriptions, you can improve your click-through rates, enhance user experience, and indirectly boost your SEO performance. Ignoring meta descriptions means missing out on these crucial benefits, potentially affecting your site’s visibility and traffic.
Poor Content Quality
Poor content quality and lack of structure can significantly impact your website’s performance, user experience, and SEO rankings. High-quality content that is well-structured not only engages readers but also signals to search engines that your site is authoritative and trustworthy. Here are the consequences of poor content quality and lack of structure, and how to avoid them.
Consequences of Poor Content Quality
- Low Engagement and High Bounce Rates
- Unengaging Content: If your content is not informative, interesting, or relevant, visitors are likely to leave quickly, leading to high bounce rates.
- User Disinterest: Poor content fails to capture the audience’s attention, resulting in low engagement metrics like time on site and pages per session.
- Negative Impact on SEO
- Lower Rankings: Search engines prioritize high-quality content. Poor content can lead to lower search engine rankings.
- Crawling and Indexing Issues: Search engines may struggle to understand and index poorly structured content, impacting your visibility.
- Reduced Credibility and Trust
- Lack of Authority: Content that is poorly written or inaccurate can damage your site’s credibility and authority.
- User Trust: Visitors may perceive your site as unreliable or untrustworthy, which can hurt your brand reputation.
- Lower Conversion Rates
- Unclear Messaging: Poor content can result in unclear or ineffective messaging, reducing the likelihood of conversions.
- User Frustration: If users cannot find the information they need easily, they are less likely to take desired actions, such as making a purchase or signing up for a newsletter.
- Higher Costs Over Time
- Increased Rework: Constantly needing to revise and improve poor content can lead to higher costs and resource expenditure.
- Missed Opportunities: Poor content can result in missed opportunities for ranking, traffic, and conversions.
Consequences of Lack of Structure
- Difficulty in Reading and Understanding
- Poor Readability: Content without a clear structure is difficult to read and understand, leading to user frustration.
- Information Overload: A lack of headings, subheadings, and paragraphs can overwhelm users, causing them to leave your site.
- Negative SEO Impact
- Crawling Challenges: Search engines rely on a clear structure to crawl and index content effectively. Poorly structured content can hinder this process.
- Ranking Issues: Content that is difficult for search engines to understand and index is less likely to rank well.
- Low User Engagement
- Navigational Issues: Users may struggle to navigate through poorly structured content, reducing their engagement and time on site.
- Reduced Interaction: Lack of structure can make it hard for users to find and interact with important information, such as call-to-action buttons.
- Inconsistent User Experience
- Confusion: Inconsistent or chaotic content structure can confuse users, leading to a poor user experience.
- Abandonment: Users are more likely to abandon a site if they cannot easily find the information they are looking for.
How to Improve Content Quality and Structure
- Focus on High-Quality Content
- Relevance: Ensure your content is relevant to your target audience and addresses their needs and interests.
- Accuracy: Provide accurate and well-researched information to establish credibility.
- Engagement: Use engaging writing styles, visuals, and multimedia elements to capture and retain user interest.
- Organize Content with Clear Structure
- Headings and Subheadings: Use headings (H1, H2, H3) to break content into manageable sections and guide users through your content.
- Paragraphs and Lists: Break text into short paragraphs and use bullet points or numbered lists to improve readability.
- Optimize for SEO
- Keywords: Incorporate relevant keywords naturally within the content, headings, and subheadings.
- Meta Tags: Use descriptive meta titles and descriptions to improve search engine visibility and click-through rates.
- Enhance Readability
- Simple Language: Use clear and concise language that is easy for your audience to understand.
- Formatting: Use bold, italics, and other formatting tools to highlight important information and improve the visual appeal.
- Regularly Update Content
- Current Information: Keep your content up-to-date with the latest information and best practices.
- Content Audits: Regularly perform content audits to identify and improve underperforming content.
- Provide Clear Calls to Action (CTAs)
- Effective CTAs: Include clear and compelling CTAs that guide users towards desired actions.
- Strategic Placement: Place CTAs strategically within the content to maximize their effectiveness.
Practical Examples
Well-Structured Blog Post
- Headings and Subheadings: Use H1 for the main title, H2 for major sections, and H3 for subsections.
- Short Paragraphs: Break content into short, digestible paragraphs for easier reading.
- Bulleted Lists: Use bulleted lists to present key points clearly and concisely.
High-Quality Product Page
- Detailed Descriptions: Provide detailed and accurate product descriptions that include relevant keywords.
- User Reviews: Include user reviews and ratings to add credibility and engage potential buyers.
- Clear CTAs: Use prominent and clear CTAs such as “Add to Cart” or “Buy Now.”
By focusing on high-quality content and clear structure, you can significantly improve user engagement, enhance SEO performance, and build credibility and trust with your audience. Investing in well-crafted content that is easy to read and navigate is essential for the success of your website.
Broken Links
Broken links, also known as dead links, are hyperlinks that no longer lead to an active webpage. These links can negatively impact both SEO and user experience. Here’s how broken links can harm your website and tips for fixing them.
How Broken Links Harm SEO and User Experience
- Negative Impact on SEO
- Crawling Issues: Search engines crawl links to discover new content. Broken links can disrupt this process, making it harder for search engines to index your site.
- Lower Rankings: A site with many broken links is seen as poorly maintained, which can lead to lower search engine rankings.
- Lost Link Equity: Broken links waste valuable link equity that could have been passed to active pages, reducing the overall SEO benefit.
- Poor User Experience
- Frustration: Users who encounter broken links may become frustrated and leave your site, leading to higher bounce rates.
- Lost Trust: Frequent broken links can make your site seem unreliable and unprofessional, damaging your credibility.
- Navigation Disruption: Broken links can disrupt the flow of navigation, making it difficult for users to find the information they need.
Tips for Fixing Broken Links
- Regularly Check for Broken Links
- Automated Tools: Use automated tools like Google Search Console, Screaming Frog, or Ahrefs to regularly scan your website for broken links.
- Manual Checks: Periodically review your site manually, especially after updates or changes, to catch any broken links that automated tools might miss.
- Update or Replace Broken Links
- Find Alternatives: Replace broken links with updated URLs that lead to relevant content.
- Redirects: Set up 301 redirects to guide users and search engines from broken URLs to new, relevant pages.
- Fix Internal Links
- Internal Linking Audit: Conduct an audit of your internal links to ensure they all point to active pages.
- Update Site Structure: Make sure your site structure is up-to-date, and remove or update links to any deleted or moved content.
- Monitor External Links
- Third-Party Content: Regularly check links to external sites to ensure they are still active and relevant.
- Replace or Remove: If an external link is broken, either find an alternative link or remove it if it no longer adds value.
- Use Custom 404 Pages
- User-Friendly 404: Create a custom 404 error page that helps users find what they’re looking for, rather than leaving them at a dead end.
- Navigation Links: Include links to popular pages or a search bar on your 404 page to help users navigate your site.
- Maintain a Link Management System
- Track Changes: Keep track of all changes to your URLs and site structure to quickly address any broken links.
- Use Plugins: For CMS platforms like WordPress, use link management plugins that can help identify and fix broken links.
Practical Examples
Using Automated Tools
- Google Search Console: Regularly check the “Coverage” and “Links” sections to identify any broken links.
- Screaming Frog: Run a site crawl to find broken links and update or replace them as needed.
Setting Up Redirects
- 301 Redirects: If a page is moved or deleted, set up a 301 redirect to guide users from the old URL to the new one.
Creating a Custom 404 Page
- Helpful Navigation: Design a 404 page with links to your homepage, popular articles, or a search function to help users find what they need.
Regular Audits
- Monthly Checks: Conduct monthly checks of your site’s internal and external links to ensure they are all functioning properly.
Using Plugins
- WordPress Plugins: Use plugins like Broken Link Checker to automatically detect and alert you of any broken links on your site.
By regularly checking for and fixing broken links, you can maintain a seamless user experience, preserve your site’s credibility, and optimize your SEO performance. Ensuring that all links on your site are functional helps keep users engaged and supports your site’s overall success.
Tools and Resources for On-Page SEO
Optimizing on-page SEO involves using various tools and resources to ensure your content, structure, and technical aspects meet best practices. Here are some top recommendations to help with on-page SEO optimization.

Keyword Research Tools
- Google Keyword Planner:
- Purpose: Find keyword ideas and get search volume data.
- Benefits: Free and integrates with Google Ads.
- Ahrefs:
- Purpose: Comprehensive keyword research, competitor analysis, and backlink tracking.
- Benefits: Offers in-depth insights and keyword difficulty scores.
- SEMrush:
- Purpose: Keyword research, competitive analysis, and rank tracking.
- Benefits: Provides extensive data on keyword trends and organic search performance.
Content Optimization Tools
- Yoast SEO (for WordPress):
- Purpose: Optimize content, meta tags, and readability.
- Benefits: Easy-to-use interface with real-time suggestions for improving on-page SEO.
- SurferSEO:
- Purpose: Optimize content based on top-ranking pages.
- Benefits: Provides guidelines for keyword usage, content length, and structure.
- Clearscope:
- Purpose: Enhance content relevance and quality.
- Benefits: Uses AI to suggest keywords and topics related to your main keyword.
Technical SEO Tools
- Google Search Console:
- Purpose: Monitor site performance, indexing status, and search queries.
- Benefits: Direct feedback from Google on your site’s health and performance issues.
- Screaming Frog SEO Spider:
- Purpose: Conduct comprehensive site audits to find broken links, duplicate content, and technical issues.
- Benefits: Offers detailed insights and exportable reports for in-depth analysis.
- GTmetrix:
- Purpose: Analyze page load speed and performance.
- Benefits: Provides detailed recommendations to improve page speed and overall site performance.
Link Management Tools
- Broken Link Checker (for WordPress):
- Purpose: Find and fix broken links on your site.
- Benefits: Automates the process of detecting broken links and missing images.
- Ahrefs Site Audit:
- Purpose: Comprehensive site audit including link health checks.
- Benefits: Identifies broken links, missing tags, and other SEO issues.
Meta Tags and Descriptions Tools
- Yoast SEO:
- Purpose: Optimize meta titles and descriptions.
- Benefits: Real-time previews and suggestions to improve click-through rates.
- SEOmofo:
- Purpose: Preview how your meta descriptions will look in search results.
- Benefits: Helps craft attractive and effective meta tags.
Analytics and Monitoring Tools
- Google Analytics:
- Purpose: Track and analyze website traffic and user behavior.
- Benefits: Provides comprehensive data on page performance, user demographics, and more.
- SEMrush:
- Purpose: Monitor keyword rankings, site audits, and competitor analysis.
- Benefits: Offers a suite of tools for continuous SEO monitoring and optimization.
Content Creation and Management Tools
- Grammarly:
- Purpose: Improve grammar, spelling, and readability of your content.
- Benefits: Enhances content quality and user experience.
- Hemingway Editor:
- Purpose: Make your writing clearer and more concise.
- Benefits: Highlights complex sentences and suggests simpler alternatives.
- WordPress:
- Purpose: Manage and publish content efficiently.
- Benefits: User-friendly and SEO-friendly with numerous plugins and customization options.
Learning and Reference Resources
- Moz Blog:
- Purpose: Stay updated with the latest SEO news and best practices.
- Benefits: Offers in-depth articles, guides, and tutorials.
- Backlinko Blog:
- Purpose: Learn advanced SEO techniques and strategies.
- Benefits: Provides detailed case studies and actionable advice.
- Google’s SEO Starter Guide:
- Purpose: Understand fundamental SEO concepts and best practices.
- Benefits: Direct guidelines from Google on how to optimize your site for search engines.
Keyword Research Tools
Keyword research is a fundamental aspect of SEO, helping you understand what terms your audience is searching for and how you can effectively target those queries. Here’s an overview of popular keyword research tools and their features.
1. Google Keyword Planner
Overview: Google Keyword Planner is a free tool provided by Google Ads that helps you discover new keywords related to your business and see estimates of the searches they receive and the cost to target them.
Features:
- Keyword Ideas: Generates keyword ideas based on a seed keyword or a website URL.
- Search Volume: Provides average monthly search volume for keywords.
- Competition: Shows the level of competition (high, medium, low) for each keyword.
- Bid Estimates: Offers suggested bid estimates for paid campaigns.
Use Case: Ideal for finding new keywords and understanding their search volume and competition levels, especially useful for planning PPC campaigns.
2. Ahrefs Keywords Explorer
Overview: Ahrefs Keywords Explorer is a comprehensive keyword research tool that provides in-depth keyword data and competitive analysis.
Features:
- Search Volume: Provides accurate search volume data.
- Keyword Difficulty: Estimates the difficulty of ranking for a keyword.
- Click Metrics: Offers data on the average number of clicks per search.
- Keyword Suggestions: Generates thousands of related keyword ideas.
- SERP Analysis: Shows the top-ranking pages for a keyword and their backlink profiles.
Use Case: Great for detailed keyword research and competitive analysis, helping you understand the potential of keywords and the effort required to rank for them.
3. SEMrush Keyword Magic Tool
Overview: SEMrush Keyword Magic Tool is a robust keyword research tool that helps you find and analyze keywords with a variety of filters and metrics.
Features:
- Keyword Suggestions: Generates a large list of related keywords.
- Search Volume: Provides search volume data for each keyword.
- Keyword Difficulty: Indicates how difficult it would be to rank for a keyword.
- SERP Features: Shows whether a keyword triggers special SERP features (e.g., featured snippets).
- Competitive Analysis: Offers insights into competitors’ keyword strategies.
Use Case: Ideal for generating extensive keyword lists and performing in-depth competitive analysis to find opportunities for ranking.
4. Ubersuggest
Overview: Ubersuggest, developed by Neil Patel, is a user-friendly keyword research tool that offers a range of features to help you find and analyze keywords.
Features:
- Keyword Suggestions: Provides keyword ideas based on a seed keyword.
- Search Volume: Displays monthly search volume for each keyword.
- SEO Difficulty: Estimates how hard it would be to rank for a keyword.
- Content Ideas: Suggests content topics related to your keywords.
- Backlink Data: Shows backlink data for top-ranking pages.
Use Case: Great for beginners and small businesses looking for an easy-to-use tool that provides essential keyword data and content ideas.
5. Moz Keyword Explorer
Overview: Moz Keyword Explorer is a powerful keyword research tool that provides insights into keyword opportunities and metrics to help you prioritize your efforts.
Features:
- Keyword Suggestions: Generates keyword ideas with related topics.
- Search Volume: Offers search volume estimates for keywords.
- Difficulty Score: Indicates the difficulty of ranking for a keyword.
- Organic CTR: Estimates the click-through rate for organic results.
- Priority Score: Combines metrics to suggest the most valuable keywords to target.
Use Case: Ideal for marketers looking for a comprehensive keyword research tool that offers unique metrics like organic CTR and priority score to help prioritize keyword targeting.
6. KeywordTool.io
Overview: KeywordTool.io is a versatile keyword research tool that generates keyword suggestions from various sources, including Google, YouTube, Bing, Amazon, and more.
Features:
- Keyword Suggestions: Provides keyword ideas from multiple search engines and platforms.
- Search Volume: Displays search volume data for each keyword (with the pro version).
- Competitive Analysis: Offers insights into competition levels for keywords.
- Long-Tail Keywords: Focuses on generating long-tail keyword suggestions.
Use Case: Excellent for finding keyword ideas across multiple platforms and search engines, particularly useful for targeting specific niches or long-tail keywords.
Practical Examples
Using Google Keyword Planner:
- Find Keywords: Enter a seed keyword or URL to generate a list of related keywords.
- Analyze Data: Review search volume, competition, and bid estimates to select the best keywords for your campaign.
Using Ahrefs Keywords Explorer:
- Keyword Analysis: Enter a keyword to see search volume, keyword difficulty, and click metrics.
- SERP Analysis: Analyze the top-ranking pages for your target keyword to understand the competition.
Using SEMrush Keyword Magic Tool:
- Generate Ideas: Enter a keyword to generate a large list of related keyword suggestions.
- Filter and Sort: Use filters to narrow down keywords based on search volume, difficulty, and SERP features.
By utilizing these keyword research tools, you can effectively identify and analyze keywords to target, helping you optimize your content for search engines and improve your SEO strategy. Each tool offers unique features that cater to different needs, from basic keyword suggestions to in-depth competitive analysis.
SEO Analysis Tools
SEO analysis tools are essential for auditing and improving on-page SEO. These tools help identify issues, provide insights, and offer recommendations to optimize your website’s performance. Here’s an overview of popular SEO analysis tools and their features.
1. Google Search Console
Overview: Google Search Console is a free tool offered by Google that helps you monitor, maintain, and troubleshoot your site’s presence in Google Search results.
Features:
- Performance Reports: Provides data on search traffic, including clicks, impressions, CTR, and average position.
- Index Coverage: Shows which pages are indexed and alerts you to any issues preventing indexing.
- Mobile Usability: Identifies mobile usability issues that could affect user experience and rankings.
- URL Inspection: Allows you to inspect individual URLs to see how Google views and indexes your page.
- Search Enhancements: Offers reports on structured data, AMP, and other search enhancements.
Use Case: Ideal for monitoring your site’s search performance, identifying and fixing indexing issues, and ensuring your site is optimized for mobile and other search enhancements.
2. Screaming Frog SEO Spider
Overview: Screaming Frog SEO Spider is a powerful website crawler that helps you audit your site’s on-page SEO elements.
Features:
- Crawl Analysis: Crawls your website to identify broken links, duplicate content, and missing meta tags.
- URL Mapping: Provides a detailed map of all URLs on your site, including status codes and page titles.
- Custom Extraction: Allows you to extract specific data from the HTML of your web pages.
- Integration: Integrates with Google Analytics, Google Search Console, and other tools for comprehensive analysis.
Use Case: Excellent for conducting in-depth technical audits of your website, identifying SEO issues, and optimizing on-page elements.
3. Ahrefs Site Audit
Overview: Ahrefs Site Audit is a comprehensive tool that scans your website for SEO issues and provides actionable recommendations.
Features:
- Health Score: Gives an overall health score based on the number and severity of SEO issues found.
- Issue Reports: Categorizes issues into different types, such as performance, HTML tags, social tags, and more.
- Detailed Insights: Provides detailed insights into each issue, explaining the problem and how to fix it.
- Regular Monitoring: Allows you to schedule regular site audits to keep track of your site’s SEO health over time.
Use Case: Ideal for identifying and fixing a wide range of SEO issues, monitoring site health, and keeping your site optimized for search engines.
4. SEMrush Site Audit
Overview: SEMrush Site Audit is a robust tool that analyzes your website for technical SEO issues and provides detailed reports.
Features:
- Site Health Score: Provides an overall site health score based on the issues detected.
- Error Categorization: Categorizes errors into warnings, errors, and notices based on their severity.
- Issue Descriptions: Offers detailed descriptions and recommendations for fixing each issue.
- Mobile and Desktop Analysis: Conducts separate audits for mobile and desktop versions of your site.
Use Case: Great for conducting comprehensive technical SEO audits, identifying issues affecting both desktop and mobile versions, and optimizing your site’s performance.
5. Moz Pro Site Crawl
Overview: Moz Pro Site Crawl helps you identify and fix SEO issues on your website to improve search engine visibility.
Features:
- Weekly Crawls: Automatically crawls your site weekly to identify new issues and track progress.
- Issue Prioritization: Prioritizes issues based on their potential impact on your site’s performance.
- Detailed Reports: Provides detailed reports on issues, including duplicate content, broken links, and missing tags.
- Custom Alerts: Allows you to set up custom alerts for specific issues.
Use Case: Ideal for ongoing site monitoring, identifying and prioritizing SEO issues, and ensuring your site remains optimized.
Practical Examples
Using Google Search Console:
- Monitor Performance: Track clicks, impressions, and average position to understand how your site performs in search.
- Fix Indexing Issues: Use the Index Coverage report to identify and fix pages that aren’t being indexed.
Using Screaming Frog SEO Spider:
- Conduct a Crawl: Run a crawl to identify broken links, missing meta tags, and duplicate content.
- Analyze Results: Review the crawl results and take action to fix identified issues.
Using Ahrefs Site Audit:
- Run an Audit: Conduct a site audit to get an overall health score and detailed reports on SEO issues.
- Implement Recommendations: Follow the provided recommendations to fix issues and improve your site’s SEO health.
Using SEMrush Site Audit:
- Perform a Site Audit: Use SEMrush to audit your site and identify technical SEO issues.
- Prioritize Fixes: Address the most critical issues first, based on the severity indicated in the report.
Using Moz Pro Site Crawl:
- Schedule Crawls: Set up weekly crawls to continuously monitor your site for SEO issues.
- Fix Issues: Review the reports and fix high-priority issues to maintain optimal site performance.
By utilizing these SEO analysis tools, you can effectively audit your website, identify and fix issues, and continuously optimize your on-page SEO. Regular use of these tools will help you stay ahead of SEO best practices and improve your site’s performance and visibility in search engines.
Content Optimization Tools
Optimizing content quality and structure is crucial for improving user engagement and SEO performance. Here are some popular tools for content optimization that help ensure your content is high-quality, well-structured, and search engine-friendly.
1. Yoast SEO (WordPress Plugin)
Overview: Yoast SEO is a popular WordPress plugin that helps you optimize your content for search engines and readability.
Features:
- SEO Analysis: Provides real-time analysis of your content, including keyword usage, meta descriptions, and readability.
- Readability Check: Offers suggestions to improve readability based on sentence length, paragraph length, and passive voice.
- Snippet Preview: Shows how your content will appear in search engine results, allowing you to optimize titles and meta descriptions.
- Content Insights: Provides insights into your content’s structure, highlighting areas for improvement.
Use Case: Ideal for WordPress users looking to optimize their content directly within their content management system, ensuring it’s SEO-friendly and easy to read.
2. Surfer SEO
Overview: Surfer SEO is a data-driven content optimization tool that helps you create content that ranks higher in search results.
Features:
- Content Editor: Provides a real-time editor with keyword recommendations and optimization tips based on top-ranking pages.
- SERP Analyzer: Analyzes search engine result pages (SERPs) to identify the key elements contributing to high rankings.
- Keyword Density: Offers keyword density recommendations to help you use keywords naturally without overstuffing.
- Content Structure: Suggests optimal content structure, including headings, paragraphs, and length, based on competitor analysis.
Use Case: Perfect for content creators and SEO professionals looking to create highly optimized content that aligns with the top-performing pages in search results.
3. ClearScope
Overview: ClearScope is an AI-powered content optimization tool that helps you create comprehensive, high-quality content.
Features:
- Keyword Recommendations: Provides keyword suggestions and topics to cover based on top-performing content.
- Content Grading: Grades your content based on coverage of recommended keywords and topics.
- Competitive Analysis: Analyzes top-ranking pages to identify gaps and opportunities in your content.
- Real-Time Feedback: Offers real-time feedback and suggestions to improve your content’s comprehensiveness and relevance.
Use Case: Ideal for creating in-depth, comprehensive content that covers all relevant topics and keywords, ensuring it stands out in search results.
4. Frase
Overview: Frase is a content optimization tool that leverages AI to help you create, optimize, and research content.
Features:
- Content Briefs: Generates detailed content briefs based on top-ranking pages, including keyword recommendations and topic outlines.
- Content Optimization: Provides real-time optimization suggestions as you write, ensuring your content is SEO-friendly and comprehensive.
- AI-Powered Research: Uses AI to research topics and generate insights that can enhance your content.
- Content Scoring: Scores your content based on keyword usage, readability, and overall quality.
Use Case: Great for content marketers and writers looking to streamline their content creation process with AI-powered insights and optimization.
5. Grammarly
Overview: Grammarly is a writing assistant that helps you improve the quality and clarity of your content.
Features:
- Grammar and Spelling Check: Detects and corrects grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors.
- Readability: Provides readability scores and suggestions to improve sentence structure and clarity.
- Tone Detector: Analyzes the tone of your content to ensure it matches your intended voice.
- Plagiarism Detection: Checks your content for plagiarism to ensure originality.
Use Case: Essential for writers looking to enhance the quality and readability of their content, ensuring it is error-free and engaging.
Practical Examples
Using Yoast SEO:
- SEO Analysis: Install the Yoast SEO plugin on your WordPress site and use the real-time analysis to optimize your content for SEO and readability.
- Snippet Preview: Adjust your meta titles and descriptions based on the snippet preview to improve click-through rates.
Using Surfer SEO:
- Content Editor: Use the content editor to write or optimize your content with real-time keyword and structure recommendations.
- SERP Analyzer: Analyze top-ranking pages to understand the elements contributing to their success and incorporate similar strategies into your content.
Using ClearScope:
- Keyword Recommendations: Generate a list of keywords and topics to cover in your content based on competitive analysis.
- Content Grading: Continuously improve your content by following ClearScope’s real-time feedback and achieving a higher content grade.
Using Frase:
- Content Briefs: Create detailed content briefs with keyword recommendations and topic outlines to guide your writing process.
- Content Optimization: Optimize your content as you write, using Frase’s real-time suggestions to ensure comprehensive coverage of relevant topics.
Using Grammarly:
- Grammar and Clarity: Write or paste your content into Grammarly to check for grammar, spelling, and readability issues.
- Tone Adjustment: Use the tone detector to ensure your content’s tone aligns with your intended voice and audience.
By leveraging these content optimization tools, you can create high-quality, well-structured content that engages readers and performs well in search engines. Regular use of these tools will help you maintain a consistent standard of excellence in your content, improving both user experience and SEO performance.
Conclusion
On-page SEO is a critical component of any successful digital marketing strategy. By focusing on the essential on-page SEO factors, you can significantly improve your search engine rankings, enhance user experience, and drive more organic traffic to your website. Implementing best practices for keyword research, content optimization, technical SEO, and user engagement can help ensure your site meets the standards set by search engines and provides value to your audience.
Recap of Key Points
- Understanding On-Page SEO: On-page SEO involves optimizing individual web pages to rank higher and earn more relevant traffic from search engines.
- Key On-Page SEO Factors: Important factors include keyword research and optimization, meta tags, content quality and relevance, header tags, internal linking, image optimization, URL structure, and mobile-friendliness.
- Common On-Page SEO Mistakes: Avoid keyword stuffing, ignoring meta descriptions, poor content quality, lack of structure, and broken links.
- Tools and Resources: Utilize tools for keyword research, SEO analysis, and content optimization to enhance your on-page SEO efforts.
Next Steps for On-Page SEO Improvement
- Conduct Thorough Keyword Research
- Use tools like Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs Keywords Explorer, and SEMrush Keyword Magic Tool to identify high-value keywords relevant to your content and audience.
- Incorporate these keywords naturally within your content, meta tags, and headers.
- Optimize Meta Tags
- Create unique, descriptive title tags and meta descriptions for each page.
- Ensure they are concise, relevant, and include primary keywords to improve click-through rates.
- Improve Content Quality and Structure
- Focus on producing high-quality, informative, and engaging content that meets user intent.
- Use clear headings, subheadings, and bullet points to structure your content for better readability and SEO.
- Enhance Technical SEO
- Regularly audit your site using tools like Google Search Console, Screaming Frog SEO Spider, and SEMrush Site Audit to identify and fix technical issues.
- Ensure your site is mobile-friendly, has fast load times, and uses clean, descriptive URLs.
- Optimize Images and Media
- Compress and resize images to reduce file sizes and improve page load speed.
- Use descriptive alt text for images to enhance accessibility and SEO.
- Improve Internal Linking
- Develop a robust internal linking strategy to guide users through your site and distribute link equity effectively.
- Link to related content to keep users engaged and improve the overall user experience.
- Regularly Update and Refresh Content
- Keep your content up-to-date with the latest information and best practices.
- Regularly review and revise existing content to ensure it remains relevant and valuable.
- Monitor and Adjust Your Strategy
- Continuously monitor your site’s performance using analytics tools like Google Analytics and Google Search Console.
- Adjust your on-page SEO strategy based on performance data and emerging trends.
By following these actionable steps, you can enhance your on-page SEO efforts, improve your search engine rankings, and create a more engaging and valuable experience for your users. Start implementing these best practices today to see positive results in your website’s performance and visibility.