What Is On Page SEO? A Beginner’s Guide
Welcome to the world of on-page SEO! If you’re just starting out with website optimization, you’re in the right place. On-page SEO, or on-site SEO, is all about tweaking and optimizing the elements of your website to make it shine in the eyes of search engines like Google. But why should you care about it? Let’s break it down.
What Is On Page SEO? On-page SEO refers to the various strategies and techniques used to optimize individual web pages. This involves adjusting both the content and HTML source code of a page to improve its visibility and relevance to search engine queries. Unlike off-page SEO, which focuses on external signals like backlinks, on-page SEO is entirely within your control.

Importance and Benefits of On-Page SEO
- Improved Search Engine Rankings: By optimizing your web pages, you increase the chances of ranking higher in search engine results pages (SERPs). Higher rankings lead to more organic traffic.
- Enhanced User Experience: On-page SEO isn’t just about pleasing search engines; it’s also about creating a better experience for your visitors. Well-structured, informative, and fast-loading pages keep users engaged and satisfied.
- Increased Click-Through Rates (CTR): Optimized meta titles and descriptions can attract more clicks from search results. A compelling snippet can make the difference between a user choosing your link over a competitor’s.
- Higher Conversion Rates: Quality content that matches user intent can lead to higher engagement and conversion rates. When visitors find exactly what they’re looking for, they’re more likely to take desired actions, like making a purchase or signing up for a newsletter.
On-page SEO is a fundamental part of any successful digital marketing strategy. It’s the foundation upon which you can build more advanced SEO tactics and achieve long-term online success.
Understanding On-Page SEO
On-page SEO is the practice of optimizing individual web pages to improve their search engine rankings and drive organic traffic. It involves tweaking various elements within your website to make it more attractive and understandable to search engines. This approach ensures that your content not only reaches a broader audience but also provides value to those who land on your site.
What Is On-Page SEO?
On-page SEO encompasses a range of tactics and techniques focused on optimizing both the content and the HTML source code of a webpage. Here’s a breakdown of its core components:
- Content Quality and Relevance: Creating high-quality, relevant content that addresses the needs and queries of your target audience.
- Keyword Optimization: Strategically using relevant keywords throughout your content to align with what users are searching for.
- Title Tags and Meta Descriptions: Crafting compelling and keyword-rich title tags and meta descriptions to improve click-through rates from search engine results pages (SERPs).
- Headings (H1, H2, H3, etc.): Structuring your content with proper headings to make it easy for search engines and users to understand the hierarchy and main points.
- URL Structure: Ensuring your URLs are clean, descriptive, and include relevant keywords.
- Internal Linking: Using internal links to connect related content within your site, which helps search engines understand the relationship between different pages.
- Image Optimization: Using descriptive file names, alt text, and reducing file sizes to improve load times and accessibility.
- User Experience (UX): Enhancing the overall user experience with fast loading times, mobile-friendliness, and easy navigation.
How On-Page SEO Differs from Off-Page SEO
While on-page SEO focuses on elements within your website, off-page SEO involves activities outside your site that impact your rankings. Here’s how they differ:
On-Page SEO:
As mentioned, this includes optimizing content, HTML source code, site architecture, and other elements directly within your control.
Off-Page SEO:
This focuses on external factors such as backlinks, social media signals, and other external endorsements that contribute to your site’s authority and credibility.
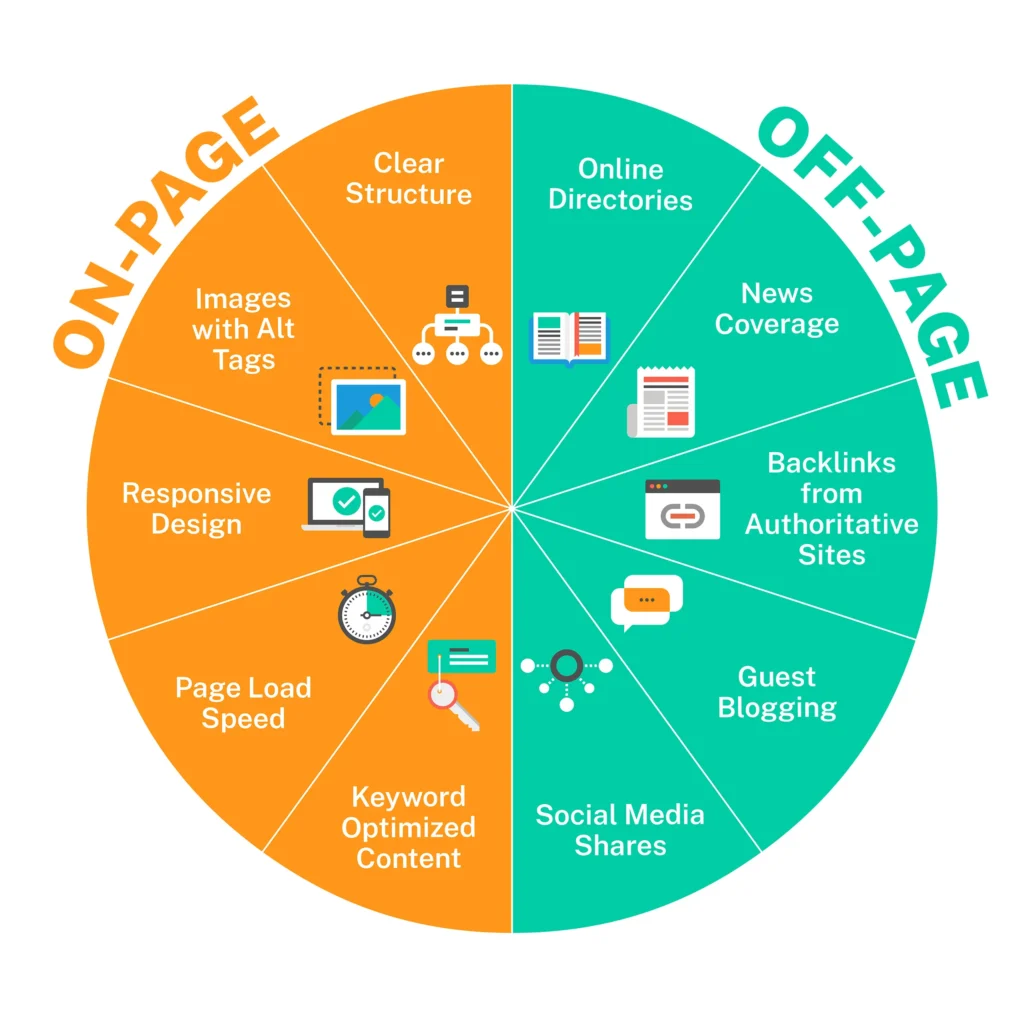
Think of on-page SEO as the foundation of your house – it’s what holds everything together and makes it strong. Off-page SEO, on the other hand, is like the neighborhood – it’s about building relationships and gaining recognition from other sites and platforms.
On-Page SEO vs. Off-Page SEO
When it comes to optimizing your website for search engines, understanding the distinction between on-page and off-page SEO is crucial. Both play essential roles in your overall SEO strategy, but they focus on different aspects of your website’s performance and online presence.
On-page SEO involves optimizing individual web pages to improve their search engine rankings and attract organic traffic. This includes both the content and HTML source code of a page.
Key Elements:
- Content Quality and Relevance: Ensuring your content is informative, engaging, and answers the queries of your target audience.
- Keyword Optimization: Incorporating relevant keywords naturally throughout your content, titles, and meta descriptions.
- Title Tags and Meta Descriptions: Crafting compelling and keyword-rich titles and meta descriptions to improve click-through rates from SERPs.
- Headings: Using proper heading tags (H1, H2, H3, etc.) to structure your content and make it easier to read.
- URL Structure: Creating clean, descriptive URLs that include relevant keywords.
- Internal Linking: Linking to other relevant pages within your site to help search engines understand the context and relationship between pages.
- Image Optimization: Using descriptive file names and alt text for images, and ensuring images are compressed for faster loading times.
- User Experience (UX): Improving site speed, mobile-friendliness, and overall navigation to enhance user satisfaction.
Off-Page SEO
Off-page SEO focuses on activities outside your website that impact your rankings. This involves improving your site’s authority and reputation through external factors.
Key Elements:
- Backlinks: Acquiring high-quality backlinks from reputable websites to boost your site’s credibility and authority.
- Social Media Engagement: Promoting your content on social media platforms to increase visibility and drive traffic.
- Guest Blogging: Writing articles for other websites to build backlinks and reach new audiences.
- Influencer Outreach: Collaborating with influencers to gain endorsements and backlinks from their networks.
- Brand Mentions: Earning mentions of your brand on other websites, even without a link, can improve your site’s authority.
Key Differences and Roles
- Control:
- On-Page SEO: Directly within your control, allowing you to make immediate changes to your website.
- Off-Page SEO: Relies on external factors and third-party sites, requiring efforts to influence and acquire endorsements.
- Focus:
- On-Page SEO: Concentrates on optimizing your website’s internal elements, such as content, structure, and user experience.
- Off-Page SEO: Emphasizes gaining external validation and signals, like backlinks and social media shares, to build your site’s authority.
- Techniques:
- On-Page SEO: Includes content optimization, meta tags, URL structure, internal linking, and improving user experience.
- Off-Page SEO: Involves link building, social media marketing, guest blogging, influencer outreach, and earning brand mentions.
Both on-page and off-page SEO are vital for a comprehensive SEO strategy. On-page SEO lays the foundation by ensuring your site is optimized and user-friendly. Off-page SEO builds upon this foundation by enhancing your site’s authority and reputation through external signals.
Why On-Page SEO Matters
On-page SEO is the cornerstone of any successful SEO strategy. It involves optimizing various elements of your website that are within your control to improve its visibility and ranking in search engine results pages (SERPs). Here’s why on-page SEO is so crucial:

Improving Search Engine Rankings
- Enhanced Visibility: Search engines like Google use complex algorithms to determine which pages should rank for specific queries. By optimizing your on-page elements, you signal to search engines that your content is relevant and valuable, improving your chances of ranking higher in SERPs.
- Keyword Optimization: Strategically placing relevant keywords in your content, headings, and meta tags helps search engines understand what your page is about. This alignment with user search intent boosts your chances of appearing in relevant searches.
- Structured Content: Using proper heading tags (H1, H2, H3, etc.) and a logical structure makes it easier for search engines to crawl and index your content. Well-structured content is more likely to be featured in rich snippets, further enhancing visibility.
- Internal Linking: Linking to other relevant pages within your site helps search engines understand the context and relationship between your pages. It also distributes link equity, which can improve the ranking of individual pages.
Boosting Click-Through Rates (CTR)
- Compelling Meta Descriptions and Titles: Well-crafted meta descriptions and titles that include relevant keywords can entice users to click on your link over others in the SERPs. Higher CTRs can also signal to search engines that your page is valuable, potentially boosting your rankings.
- Rich Snippets: By using structured data, you can enhance your search listings with rich snippets, such as review stars, images, and other information. These enhanced listings can stand out in search results, increasing your CTR.
Increasing Conversion Rates
- Matching User Intent: By optimizing your content to meet the specific needs and queries of your audience, you can attract more qualified traffic. When visitors find exactly what they’re looking for, they are more likely to take desired actions, such as making a purchase or signing up for a newsletter.
- Trust and Credibility: High-quality content and a well-optimized site can establish trust and credibility with your audience. A trustworthy site can lead to higher conversion rates as users feel more confident in engaging with your business.
On-page SEO is essential for both search engine rankings and user experience. By optimizing your content and website structure, you make it easier for search engines to understand and index your site while providing a better experience for your visitors. This dual focus on search engines and users creates a strong foundation for your SEO strategy, driving organic traffic, increasing engagement, and boosting conversions.
Enhancing Visibility
On-page SEO is a powerful tool for enhancing the visibility of your website in search engine results. By optimizing various elements of your site, you can improve its ranking and make it more attractive to both search engines and users. Here’s how on-page SEO enhances visibility:
- Keyword Optimization:
- Relevance: Incorporating relevant keywords in strategic locations such as titles, headings, and body content helps search engines understand what your page is about. This alignment with search queries increases the chances of your page appearing in relevant search results.
- Density: While keyword stuffing is a big no-no, using keywords naturally and appropriately throughout your content can boost your page’s relevance for those terms.
- Title Tags and Meta Descriptions:
- Title Tags: A well-crafted title tag that includes the primary keyword can significantly impact your page’s visibility. Title tags are one of the most important on-page SEO elements as they tell search engines and users what the page is about.
- Meta Descriptions: Although not a direct ranking factor, meta descriptions influence click-through rates (CTR). A compelling meta description that includes relevant keywords can entice users to click on your link, which indirectly boosts visibility.
- Headings and Subheadings:
- Structured Content: Using proper heading tags (H1, H2, H3, etc.) to organize your content helps search engines understand the structure and main points of your page. This makes it easier for them to crawl and index your site, improving your chances of ranking well.
- Keyword Placement: Including keywords in your headings and subheadings reinforces the relevance of your content to specific search queries.
- Internal Linking:
- Contextual Relevance: Linking to other relevant pages within your site helps search engines understand the relationship between different pieces of content. This context can enhance the visibility of linked pages by distributing link equity.
- Crawlability: Internal links make it easier for search engines to crawl your site and discover new or updated content, ensuring all your important pages are indexed.
- URL Structure:
- Descriptive URLs: Clean and descriptive URLs that include relevant keywords provide both search engines and users with clear information about the page’s content. This can improve click-through rates and help search engines categorize your content correctly.
- Image Optimization:
- Alt Text: Adding descriptive alt text to images helps search engines understand what the images are about, which can enhance your page’s relevance for certain search queries.
- File Names: Using keyword-rich file names for your images can further boost the page’s visibility.
Improving User Experience
On-page SEO is not just about pleasing search engines; it’s also about creating a seamless and enjoyable experience for your visitors. Here’s how on-page SEO contributes to a better user experience:
- Quality Content:
- Engagement: High-quality, informative, and engaging content keeps visitors on your site longer. This reduces bounce rates and increases the likelihood of conversions.
- Relevance: Content that directly addresses the needs and queries of your audience builds trust and satisfaction, encouraging users to return.
- Site Speed:
- Load Times: Optimizing images, using efficient coding practices, and leveraging browser caching can significantly improve page load times. Faster-loading pages enhance user experience by reducing wait times and frustration.
- Performance: A speedy site is not only good for users but also a ranking factor for search engines, making it a win-win situation.
- Mobile-Friendliness:
- Responsive Design: Ensuring your website is mobile-friendly is crucial in today’s mobile-first world. A responsive design adapts to different screen sizes, providing a smooth experience for users on any device.
- Accessibility: Mobile optimization also includes making your site accessible to all users, regardless of their device or abilities.
- Clear Navigation:
- Ease of Use: A well-organized site structure with clear navigation menus helps users find what they’re looking for quickly and easily. This improves user satisfaction and encourages them to explore more of your site.
- Breadcrumbs: Using breadcrumbs can help users understand their location within your site’s hierarchy, making navigation intuitive.
- Visual Appeal:
- Engaging Media: Using high-quality images, videos, and graphics can make your content more appealing and engaging. Visual elements break up text and keep users interested.
- Readability: Optimizing typography, spacing, and overall design enhances readability, making it easier for users to consume your content.
- Internal Linking:
- Content Discovery: Internal links guide users to related content, helping them discover more of your site’s offerings and keeping them engaged longer.
- User Journey: Thoughtful internal linking can enhance the user journey by providing additional resources and information that are relevant to their interests.
On-page SEO plays a critical role in both enhancing the visibility of your website in search engine results and improving the user experience. By focusing on these elements, you can create a site that is not only optimized for search engines but also provides a valuable and enjoyable experience for your visitors. This dual focus ultimately leads to higher rankings, more organic traffic, and greater user satisfaction.
Key Elements of On-Page SEO
On-page SEO involves various elements that collectively improve a website’s search engine visibility and user experience. Here’s an overview of the key components:
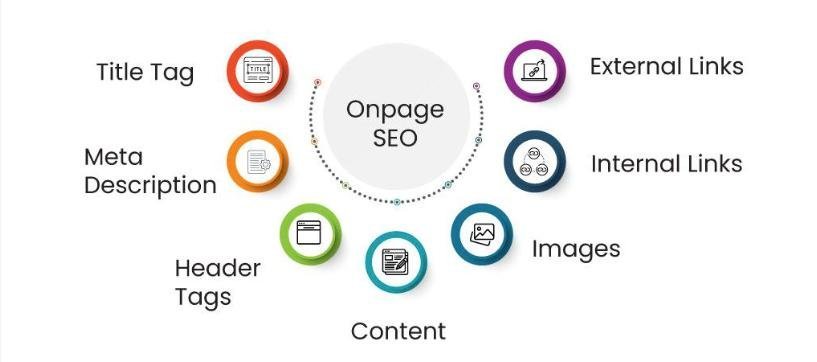
- Content Quality and Relevance: High-quality, engaging content that addresses user queries and provides value.
- Keyword Optimization: Strategic placement of relevant keywords throughout the content.
- Title Tags and Meta Descriptions: Compelling and keyword-rich titles and descriptions that improve click-through rates.
- Headings and Subheadings: Proper use of heading tags to structure content and enhance readability.
- URL Structure: Clean, descriptive URLs that include relevant keywords.
- Internal Linking: Linking to other relevant pages within the site to improve navigation and context.
- Image Optimization: Descriptive alt text, file names, and compressed images for faster loading times.
- User Experience (UX): Enhancing site speed, mobile-friendliness, and overall navigation.
- Schema Markup: Implementing structured data to help search engines understand the content and enhance search results with rich snippets.
Keyword Research and Integration
Keyword research is the foundation of any successful SEO strategy. It involves identifying the search terms that users enter into search engines when looking for information, products, or services related to your niche. Here’s why keyword research is crucial:
- Understanding User Intent: Keywords reveal what your target audience is searching for, helping you create content that meets their needs.
- Competitive Analysis: Analyzing keyword competition helps you identify opportunities and gaps in the market.
- Content Strategy: Keywords guide your content creation, ensuring that you address topics that are relevant and in demand.
- Improved Rankings: Targeting the right keywords increases your chances of ranking higher in search engine results pages (SERPs).
Best Practices for Integrating Keywords
- Identify Primary and Secondary Keywords:
- Primary Keywords: Focus on the main keyword that best represents the page’s content. This should be included in strategic locations such as the title tag, URL, and first paragraph.
- Secondary Keywords: Use related keywords and variations throughout the content to provide context and support the primary keyword.
- Natural Integration:
- Avoid Keyword Stuffing: Overusing keywords can lead to poor readability and potential penalties from search engines. Aim for a natural flow that prioritizes user experience.
- Synonyms and Variations: Use synonyms and related terms to avoid repetitive content and improve readability.
- Strategic Placement:
- Title Tag: Include the primary keyword near the beginning of the title tag.
- Meta Description: Write a compelling meta description that incorporates the primary keyword naturally.
- Headings: Use keywords in headings and subheadings to structure the content and signal its relevance.
- Introduction and Conclusion: Place the primary keyword in the introduction and conclusion to reinforce the page’s main topic.
- Body Content: Distribute keywords evenly throughout the content, maintaining a natural flow.
- Use of LSI Keywords:
- Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) Keywords: These are related terms and phrases that provide context to your content. Incorporating LSI keywords helps search engines understand the depth and breadth of your content.
- Optimize Images and Alt Text:
- File Names: Use descriptive, keyword-rich file names for images.
- Alt Text: Include keywords in the alt text to improve accessibility and search engine understanding of the image content.
- Internal and External Linking:
- Internal Links: Link to other relevant pages on your site using anchor text that includes keywords.
- External Links: Link to reputable external sources that provide additional context and value to your content.
Identifying Target Keywords
Choosing the right target keywords is a crucial step in on-page SEO. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you identify and select the most effective keywords for your content:
1. Understand Your Audience
- Know Your Niche: Start by understanding your industry, niche, and the type of content your target audience is looking for.
- User Intent: Identify the intent behind potential search queries. Are users looking for information, a specific product, or a solution to a problem?
2. Conduct Keyword Research
- Brainstorm Seed Keywords: List out basic terms and phrases related to your niche. These seed keywords will form the foundation of your keyword research.
- Use Keyword Tools: Utilize keyword research tools like Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Ubersuggest to find keywords related to your seed terms. These tools provide data on search volume, competition, and related keywords.
3. Analyze Competitors
- Identify Competitors: Find out who your main competitors are in the search results for your target topics.
- Analyze Their Keywords: Use tools like Ahrefs or SEMrush to analyze the keywords your competitors are ranking for. This can give you insights into potential keywords you might have missed.
4. Evaluate Keyword Metrics
- Search Volume: Look for keywords with a decent search volume. High search volume indicates that many users are searching for that term.
- Competition: Assess the competition level for each keyword. High-competition keywords might be harder to rank for, especially if you’re just starting out.
- Relevance: Ensure the keywords you choose are highly relevant to your content and audience.
5. Select Long-Tail Keywords
- Long-Tail Keywords: These are longer, more specific phrases that often have lower search volume but higher intent and lower competition. They can be easier to rank for and attract more targeted traffic.
6. Group Keywords by Topic
- Keyword Clustering: Group related keywords into clusters or themes. This helps in creating comprehensive content that covers a topic thoroughly and improves overall site structure.
Natural Keyword Placement
Once you have identified your target keywords, the next step is to integrate them naturally into your content. Here are some best practices for natural keyword placement:
1. Use Keywords in Key Locations
- Title Tag: Place your primary keyword at the beginning of the title tag if possible. This helps search engines and users quickly understand what your page is about.
- Meta Description: Write a compelling meta description that includes your primary keyword. This can improve click-through rates from SERPs.
- Headings: Use your primary keyword in the H1 tag and include secondary keywords in H2 and H3 tags to structure your content.
2. Natural Flow in Content
- Introduction: Include your primary keyword in the first 100-150 words of your content to establish relevance early on.
- Body Text: Distribute your keywords evenly throughout the content. Avoid keyword stuffing and ensure that the text reads naturally.
- Synonyms and Variations: Use synonyms and related terms to keep the content engaging and avoid repetitive keyword use.
3. Optimize for LSI Keywords
- Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) Keywords: These are related terms that add context to your primary keyword. Including LSI keywords helps search engines understand the full scope of your content.
- Contextual Integration: Use LSI keywords naturally within the content where they fit contextually.
4. Enhance Readability
- Short Paragraphs: Break content into short paragraphs to improve readability.
- Bullet Points and Lists: Use bullet points and numbered lists to make the content easier to scan.
- Visual Content: Include images, infographics, and videos with optimized alt text that incorporates keywords.
5. Internal Linking
- Relevant Anchor Text: Use keywords in the anchor text of internal links to related pages on your site. This helps with keyword relevance and site navigation.
- Natural Context: Ensure that the internal links fit naturally within the content and provide additional value to the reader.
Identifying target keywords and placing them naturally within your content is essential for effective on-page SEO. By understanding your audience, conducting thorough keyword research, and integrating keywords seamlessly, improving On-Page SEO enhances your site’s visibility in search results and provide a better user experience. This dual approach ensures that your content is both search engine-friendly and engaging for your readers.
Meta Tags Optimization
Meta tags, including title tags and meta descriptions, are critical components of on-page SEO. They play a significant role in helping search engines understand the content of a webpage and influence users’ decisions to click on a link in search engine results pages (SERPs).
Title Tags: The title tag is an HTML element that specifies the title of a web page. It’s displayed on SERPs as the clickable headline for a given result and is also used in the browser’s title bar when the page is open.
Impact on SEO:
- Relevance: Title tags help search engines understand the context of the page. A well-crafted title tag that includes relevant keywords can improve the page’s relevance for specific search queries.
- Ranking Factor: Although not the sole factor, title tags are a crucial element that search engines consider when determining rankings.
- User Experience: A clear and descriptive title tag can improve user experience by accurately describing the page’s content, leading to higher click-through rates (CTR).
Meta Descriptions: The meta description is an HTML element that provides a brief summary of a webpage’s content. It appears below the title tag on SERPs and is intended to give users a preview of the page’s content.
Impact on SEO:
- CTR Influence: While meta descriptions are not a direct ranking factor, they significantly influence click-through rates. A compelling meta description can attract more clicks, signaling to search engines that the page is valuable and relevant.
- User Engagement: A well-written meta description sets the right expectations for users, leading to better engagement and reduced bounce rates.
Crafting Effective Title Tags
Creating effective and SEO-friendly title tags involves several best practices:
- Incorporate Primary Keywords:
- Include your primary keyword near the beginning of the title tag. This helps search engines understand the main topic of the page and can improve rankings for that keyword.
- Keep It Concise:
- Limit the length to about 50-60 characters. Longer titles may get cut off in SERPs, leading to incomplete information being displayed.
- Ensure Relevance:
- Make sure the title accurately reflects the content of the page. Misleading titles can lead to high bounce rates, negatively impacting SEO.
- Make It Compelling:
- Write a title that grabs attention and entices users to click. Use power words and phrases that evoke curiosity or provide value.
- Avoid Keyword Stuffing:
- Use keywords naturally and avoid cramming too many into the title tag. Keyword stuffing can lead to penalties and poor user experience.
- Use Branding Wisely:
- If appropriate, include your brand name at the end of the title tag. This can enhance brand recognition and trust.
Writing Compelling Meta Descriptions
Here are some guidelines for writing meta descriptions that improve click-through rates:
- Summarize Content Effectively:
- Provide a clear and concise summary of what users can expect to find on the page. Aim for 150-160 characters to ensure the entire description is displayed in SERPs.
- Include Primary Keywords:
- Incorporate your primary keyword and relevant secondary keywords naturally. This helps users and search engines understand the topic and relevance of your page.
- Focus on User Intent:
- Write with the user’s intent in mind. Address the needs or queries that brought them to search in the first place.
- Use a Call to Action (CTA):
- Encourage users to click on your link by including a compelling CTA. Phrases like “Learn more,” “Discover,” “Get started,” or “Find out” can motivate users to take action.
- Highlight Unique Selling Points (USPs):
- Emphasize what makes your content unique or valuable. This could be special features, benefits, or insights that set your page apart from competitors.
- Create a Sense of Urgency:
- Where appropriate, create a sense of urgency with phrases like “Limited time,” “Don’t miss out,” or “Act now.”
- Test and Optimize:
- Regularly review and update your meta descriptions based on performance. A/B testing different versions can help identify the most effective descriptions.
Optimizing meta tags, including title tags and meta descriptions, is essential for improving your website’s visibility and click-through rates. Effective title tags enhance relevance and rankings, while compelling meta descriptions attract clicks and engage users. By following these best practices, you can create meta tags that boost your SEO performance and provide a better user experience.
Content Quality and Structure
High-quality content and structured formatting are essential components of on-page SEO. They not only help improve your search engine rankings but also enhance user experience, making your content more engaging and easier to read. Here’s why they matter and how you can leverage them for better SEO performance.
Importance of High-Quality Content
- Relevance and Authority:
- Search Engines: High-quality content that is relevant and authoritative is favored by search engines. It helps establish your site as a credible source of information, improving your chances of ranking higher.
- Users: Content that provides value and answers users’ queries builds trust and encourages repeat visits, boosting overall site engagement.
- User Engagement:
- Time on Page: Engaging content keeps users on your page longer, reducing bounce rates and signaling to search engines that your content is valuable.
- Social Sharing: Quality content is more likely to be shared on social media, increasing your reach and attracting more traffic.
- Conversion Rates:
- Trust and Credibility: Informative and well-researched content builds trust with your audience, leading to higher conversion rates for products, services, or other calls to action.
Creating Valuable Content
Creating valuable and informative content involves understanding your audience and addressing their needs effectively. Here’s how to do it:
- Know Your Audience:
- Research: Conduct audience research to understand their needs, preferences, and pain points. Use tools like surveys, social media insights, and analytics data.
- Personas: Create detailed buyer personas to guide your content creation process.
- Satisfy Search Intent:
- Intent Types: Identify the type of search intent (informational, navigational, transactional, or commercial) behind the keywords you are targeting and tailor your content accordingly.
- Answer Questions: Provide clear and comprehensive answers to common questions and queries related to your topic.
- Comprehensive Coverage:
- Depth: Cover your topic in-depth, providing detailed information, insights, and examples. This not only helps with SEO but also positions you as an expert in your field.
- Variety: Use a mix of text, images, videos, and infographics to make your content more engaging and cater to different learning styles.
- Originality and Uniqueness:
- Unique Insights: Offer unique perspectives, insights, and original research to stand out from competitors.
- Avoid Plagiarism: Ensure your content is original and not copied from other sources. Use plagiarism-checking tools if necessary.
- Actionable Information:
- Practical Tips: Provide actionable tips, steps, or advice that readers can implement immediately.
- Clear Takeaways: Summarize key points and takeaways to reinforce learning and retention.
Using Headers and Subheaders
Proper use of headers (H1, H2, H3) and subheaders helps organize your content, making it easier for both users and search engines to understand. Here are best practices for using headers and subheaders effectively:
- H1 Tag:
- Main Title: Use the H1 tag for the main title of your page. It should be descriptive and include the primary keyword.
- Unique and Relevant: Ensure each page has a unique H1 that accurately reflects its content.
- H2 Tags:
- Subsections: Use H2 tags for major subsections of your content. These should break down the main topic into smaller, related topics.
- Keyword Integration: Incorporate relevant keywords naturally in H2 tags to improve SEO.
- H3 and Beyond:
- Further Breakdown: Use H3 tags (and H4, H5, etc., if necessary) for further breaking down subsections into smaller parts. This helps in creating a clear hierarchy and logical flow.
- Descriptive: Ensure that each subheader is descriptive and informative, giving readers a clear idea of what to expect in that section.
- Readability and Flow:
- Logical Structure: Organize your content logically, using headers to guide readers through the text. This enhances readability and makes it easier for users to find the information they need.
- Scannability: Well-structured content with clear headers and subheaders is easier to scan, helping users quickly locate the sections they’re interested in.
- SEO Benefits:
- Crawlability: Search engines use headers to understand the structure and hierarchy of your content. Proper use of headers can improve your site’s crawlability and indexing.
- Featured Snippets: Well-structured content is more likely to be featured in search engine snippets, which can significantly boost visibility.
High-quality content and structured formatting are vital for both user engagement and SEO performance. By creating valuable content that satisfies search intent and using headers and subheaders to organize it, you enhance readability, improve search engine rankings, and provide a better user experience. This comprehensive approach ensures your content is both search engine-friendly and engaging for your audience.
Internal Linking
Internal linking is a fundamental aspect of on-page SEO that involves connecting different pages within your website. This practice not only helps search engines understand the structure of your site but also enhances user navigation and experience. Here’s a closer look at the benefits of internal linking and strategies for effective internal link building.
Benefits of Internal Linking
- Improved Crawlability:
- Search Engines: Internal links help search engines crawl and index your site more efficiently. They provide pathways for search engines to discover new and updated content.
- Comprehensive Indexing: Ensuring that all important pages are linked internally helps them get indexed and ranked.
- Enhanced User Experience:
- Navigation: Internal links guide users to related content, improving their overall experience by helping them find additional information quickly.
- Engagement: By providing relevant links, you keep users engaged on your site longer, reducing bounce rates and increasing the chances of conversions.
- Distributed Link Equity:
- Page Authority: Internal links distribute link equity (ranking power) throughout your site, helping to boost the authority of individual pages.
- Supporting Pages: Linking to less authoritative pages from higher authority pages can help improve their ranking potential.
- Context and Relevance:
- Topical Relevance: Internal links provide context and help search engines understand the relationship between different pieces of content.
- Keyword Targeting: Using relevant anchor text in internal links can enhance the keyword relevance of the linked pages.
Strategies for Effective Internal Link Building
- Link to Relevant Content:
- Relevance: Ensure that the linked pages are contextually relevant to the content. This enhances the user experience and provides valuable information.
- Value: Links should offer additional value to the reader, guiding them to more in-depth information or related topics.
- Use Descriptive Anchor Text:
- Clarity: Use clear and descriptive anchor text that indicates what the linked page is about. Avoid generic phrases like “click here.”
- Keywords: Incorporate relevant keywords in the anchor text, but ensure it flows naturally within the content.
- Prioritize High-Value Pages:
- Important Pages: Link to high-value pages, such as cornerstone content, product pages, or other key pages you want to rank higher.
- Strategic Placement: Place internal links within the body of your content where they are more likely to be clicked, rather than in footers or sidebars.
- Balance Internal and External Links:
- Internal Focus: While external links are important, maintaining a balance with a strong internal linking strategy ensures that link equity stays within your site.
- Natural Integration: Integrate internal links naturally within the content to maintain a smooth reading experience.
Linking to Relevant Pages
- Content Hubs:
- Cluster Topics: Create content hubs where related articles are linked together. This thematic clustering helps search engines understand the topical relevance and authority of your site.
- Pillar Pages: Develop pillar pages that provide comprehensive coverage of a broad topic and link to related subtopics or articles.
- Related Articles:
- Suggestions: At the end of an article, suggest related articles that the reader might find interesting. This encourages users to stay longer on your site.
- Contextual Links: Within the content, link to other articles that provide additional context or further reading on a particular point.
- Navigation Menus:
- Main Menu: Include links to important pages in your main navigation menu. This ensures they are easily accessible and signals their importance to search engines.
- Breadcrumbs: Use breadcrumb navigation to help users understand their location within your site’s hierarchy and easily navigate back to higher-level pages.
Creating a Logical Link Structure
- Hierarchical Structure:
- Top-Down Approach: Organize your site content in a hierarchical manner, with broad topics at the top and more specific subtopics beneath. Use internal links to connect these layers logically.
- Parent-Child Relationship: Ensure that each subpage links back to its parent page and vice versa, maintaining a clear and logical hierarchy.
- Siloing:
- Thematic Silos: Group related content into silos or clusters based on themes or topics. Internally link within each silo to reinforce the topical relevance.
- Clear Boundaries: While linking within silos, ensure that cross-silo links are minimal to maintain thematic integrity.
- Consistent Internal Links:
- Regular Updates: Regularly review and update internal links to ensure they remain relevant and functional.
- Avoid Orphan Pages: Make sure every page on your site is linked to from at least one other page. Orphan pages (pages with no internal links) are hard to find and rank poorly.
- Internal Link Audit:
- Tools: Use SEO tools like Screaming Frog, Ahrefs, or SEMrush to conduct an internal link audit. Identify broken links, orphan pages, and opportunities for better link distribution.
- Optimization: Regularly optimize your internal link structure based on audit results to improve site navigation and SEO performance.
Internal linking is a powerful on-page SEO technique that enhances both search engine rankings and user experience. By linking to relevant pages, using descriptive anchor text, and maintaining a logical link structure, you can distribute link equity effectively and improve site navigation. This comprehensive approach ensures that your content is easily discoverable and engaging, leading to higher rankings and better user satisfaction.
Image Optimization
Image optimization is a crucial aspect of on-page SEO that can significantly improve your website’s speed, user experience, and search engine rankings. Properly optimized images load faster and are easier for search engines to understand, leading to better overall performance.
Techniques for Optimizing Images
- Use the Right File Format:
- JPEG: Ideal for photographs and images with many colors. JPEG files are typically smaller in size.
- PNG: Best for images that require transparency and those with fewer colors, such as logos and icons. PNG files are usually larger but offer higher quality.
- WebP: A modern format that provides superior compression and quality compared to JPEG and PNG.
- Proper Dimensions:
- Scale Images: Resize images to the exact dimensions needed for display on your site. Avoid using larger images and then scaling them down with HTML or CSS, as this increases load times.
- Responsive Images: Use the
srcsetattribute to serve different image sizes based on the user’s device, ensuring faster loading times on mobile devices.
- Compression:
- Lossy Compression: Reduces file size by permanently removing some data, which can slightly affect image quality. Suitable for web use where speed is critical.
- Lossless Compression: Reduces file size without losing any data, preserving image quality. Ideal for images where quality cannot be compromised.
- Tools: Use tools like TinyPNG, JPEG-Optimizer, or Photoshop’s “Save for Web” feature to compress images before uploading.
Using Alt Text
Alt text (alternative text) is a brief description of an image used by search engines and screen readers to understand what the image represents. Here’s why it’s important and how to write effective alt text:
Importance of Alt Text
- Accessibility:
- Screen Readers: Alt text helps visually impaired users understand the content of images through screen readers.
- Compliance: Providing alt text is a key aspect of web accessibility guidelines (WCAG), ensuring your site is accessible to all users.
- SEO:
- Image Search: Alt text helps search engines index images correctly, increasing the chances of your images appearing in search results.
- Context: Alt text provides additional context to search engines about the content of your page, potentially improving rankings.
Best Practices for Writing Alt Text
- Be Descriptive and Concise:
- Specific Description: Clearly describe what the image depicts in a concise manner. Aim for a brief but informative description.
- Avoid Redundancy: Don’t start with phrases like “image of” or “picture of,” as search engines and screen readers already know it’s an image.
- Use Keywords Wisely:
- Relevance: Include relevant keywords naturally within the alt text, but avoid keyword stuffing.
- Context: Ensure the keywords fit contextually with the image and the surrounding content.
- Functionality:
- Informative: If the image is functional (e.g., a button or link), describe its function, such as “search icon” or “download button.”
Reducing Image File Size
Reducing image file size is essential for improving site speed without compromising quality. Here are some methods to achieve this:
- Compression Tools:
- Online Tools: Use tools like TinyPNG, JPEG-Optimizer, and ImageOptim to compress images without significant quality loss.
- Software: Utilize software like Adobe Photoshop, GIMP, or Lightroom to compress images during the editing process.
- Use Appropriate Resolution:
- Web Resolution: For web use, 72 DPI (dots per inch) is typically sufficient. Higher resolutions are unnecessary and increase file size.
- Display Size: Ensure images are saved at the correct display size. For example, if an image will be displayed at 800×600 pixels, save it at that size rather than uploading a larger version.
- Leverage Lazy Loading:
- Lazy Loading: Implement lazy loading to delay the loading of images until they are needed (i.e., when they appear in the user’s viewport). This improves initial load times and saves bandwidth.
- Serve Scaled Images:
- Responsive Images: Use the
srcsetattribute in the<img>tag to serve appropriately sized images based on the user’s device and screen resolution. This ensures that mobile users are not served unnecessarily large images.
- Responsive Images: Use the
- WebP Format:
- WebP: Consider using the WebP format, which provides superior compression and quality compared to older formats like JPEG and PNG. Many modern browsers support WebP, and it can significantly reduce file sizes.
Optimizing images is vital for improving your website’s speed, SEO, and user experience. By using the right file formats, compressing images, and employing alt text effectively, you can ensure your images load quickly and contribute positively to your site’s performance. Additionally, reducing image file sizes without compromising quality enhances accessibility and engagement, making your site more user-friendly and search engine-friendly.
URL Structure
Creating clean and SEO-friendly URL structures is essential for improving your website’s indexing and ranking. Well-structured URLs are easier for search engines to crawl and understand, and they provide a better user experience by clearly indicating the content of a page. Here’s how to create effective URL structures:
Creating Clean and SEO-Friendly URL Structures
- Keep URLs Simple and Descriptive:
- Short and Sweet: Aim for shorter URLs that are easy to read and remember. Avoid overly long URLs that can confuse both users and search engines.
- Descriptive: Ensure that your URLs accurately describe the content of the page. This helps users and search engines understand what to expect.
- Use Keywords Appropriately:
- Primary Keyword: Incorporate the primary keyword for the page within the URL. This boosts relevance and helps with SEO.
- Avoid Keyword Stuffing: Use keywords naturally and avoid stuffing multiple keywords into the URL.
- Use Hyphens to Separate Words:
- Readability: Use hyphens (-) to separate words in the URL. This improves readability for both users and search engines.
- Avoid Underscores: Avoid using underscores (_) as they are not as easily recognized by search engines as word separators.
- Maintain a Logical Hierarchy:
- Site Structure: Reflect the site’s hierarchy in the URL structure. For example, use categories and subcategories to organize content logically.
- Breadcrumb URLs: Consider using breadcrumb-style URLs that show the path to the content, enhancing both user experience and SEO.
Crafting Descriptive URLs
- Include Relevant Keywords:
- Primary Keywords: Ensure the URL includes primary keywords that are relevant to the page content. This helps search engines understand the topic of the page.
- Contextual Keywords: Use keywords that fit naturally and provide context to the content.
- Avoid Stop Words:
- Conciseness: Remove unnecessary stop words (e.g., “and,” “or,” “but”) from the URL to keep it concise. However, if removing a stop word makes the URL less readable or changes its meaning, it’s better to keep it.
- Reflect Content:
- Accuracy: Make sure the URL accurately reflects the content of the page. Avoid using generic URLs that do not convey specific information about the page.
- Be Consistent:
- URL Structure: Maintain a consistent URL structure throughout your site. Consistency helps search engines understand and index your site more effectively.
Avoiding Unnecessary Parameters
- Simplify URLs:
- Minimal Parameters: Avoid using unnecessary parameters in the URL, such as session IDs or tracking codes, which can make the URL look cluttered and complex.
- Clean URLs: Use clean URLs that are free from extraneous characters and parameters.
- Static Over Dynamic:
- Static URLs: Prefer static URLs over dynamic ones. Static URLs remain the same for each page load, while dynamic URLs can change based on parameters.
- Rewrite Rules: Use URL rewriting techniques to convert dynamic URLs into static ones, improving readability and SEO.
- Canonicalization:
- Canonical Tags: Use canonical tags to indicate the preferred version of a URL when multiple versions exist. This helps prevent duplicate content issues and consolidates ranking signals.
- Parameter Handling:
- Google Search Console: Use Google Search Console to specify how URL parameters should be handled. This can help search engines better understand and crawl your site.
Creating clean, descriptive, and keyword-rich URLs is a key aspect of on-page SEO. By keeping URLs simple and avoiding unnecessary parameters, you can improve your site’s indexing and ranking while providing a better user experience. A logical and consistent URL structure ensures that both search engines and users can easily navigate and understand your site’s content.
Common On-Page SEO Mistakes to Avoid
On-page SEO is critical for improving your website’s visibility and user experience, but it’s easy to make mistakes that can hinder your efforts. Here are some common on-page SEO mistakes and how to avoid them:
Keyword Stuffing
Explanation:
- What It Is: Keyword stuffing involves overloading a webpage with keywords in an attempt to manipulate its ranking in search engine results. This includes placing too many keywords in the content, title tags, meta descriptions, and alt text.
- Why It Should Be Avoided:
- User Experience: Keyword-stuffed content often reads poorly and can be off-putting to users.
- SEO Penalties: Search engines like Google penalize keyword stuffing, which can result in lower rankings or removal from search results.
How to Avoid:
- Natural Integration: Use keywords naturally within the content. Focus on providing value and ensuring the content reads well.
- Synonyms and Variations: Use synonyms and related terms to avoid repetition and maintain readability.
- Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI): Incorporate LSI keywords to add context and depth without overloading the primary keyword.
Ignoring Meta Descriptions
Explanation:
- What It Is: Ignoring or neglecting to write meta descriptions means missing out on the opportunity to provide a summary of your page’s content for search engines and users.
- Impact on SEO:
- CTR: Compelling meta descriptions can significantly improve click-through rates from search engine results pages (SERPs).
- Relevance: Meta descriptions help users understand the relevance of your page to their query, which can improve user engagement.
How to Avoid:
- Write Unique Descriptions: Ensure each page has a unique and compelling meta description that accurately summarizes the content.
- Include Keywords: Incorporate primary keywords naturally within the meta description to highlight the relevance of the page.
- Call to Action: Use a call to action to entice users to click on your link, such as “Learn more,” “Discover,” or “Get started.”
Poor Content Quality
Explanation:
- What It Is: Poor content quality includes thin, irrelevant, or unengaging content that fails to provide value to users.
- Consequences:
- User Engagement: Low-quality content leads to high bounce rates and low time on page, signaling to search engines that the content is not valuable.
- Rankings: Search engines prioritize high-quality, relevant content, and poor content can result in lower rankings.
How to Avoid:
- Create Valuable Content: Focus on creating informative, engaging, and high-quality content that addresses the needs and queries of your audience.
- Structure: Use headings, subheadings, bullet points, and images to structure the content and make it easy to read and navigate.
- Regular Updates: Keep your content updated and relevant by regularly reviewing and refreshing it.
Broken Links
Explanation:
- What It Is: Broken links are hyperlinks that lead to non-existent pages (404 errors). These can occur due to deleted pages, changed URLs, or typos in the link.
- Impact on SEO:
- User Experience: Broken links frustrate users and can lead to high bounce rates.
- Crawlability: Search engines may struggle to crawl your site effectively, leading to poor indexing.
How to Avoid:
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits of your site to identify and fix broken links. Tools like Screaming Frog, Ahrefs, or Google Search Console can help detect broken links.
- Update Links: Ensure all internal and external links are updated and pointing to the correct pages.
- Redirects: Use 301 redirects for any pages that have been moved or deleted to ensure users and search engines are directed to the correct page.
Avoiding common on-page SEO mistakes is crucial for maintaining a high-performing website. By steering clear of keyword stuffing, ensuring you write meta descriptions, focusing on high-quality content, and regularly checking for broken links, you can enhance both your search engine rankings and user experience.
Tools and Resources for On-Page SEO
Optimizing on-page SEO involves various tasks, from keyword research to content optimization and site auditing. Using the right tools and resources can make these tasks more efficient and effective. Here are some recommended tools and resources for on-page SEO optimization:
Keyword Research Tools
- Google Keyword Planner
- Features: Provides keyword suggestions, search volume data, and competition levels. It’s free and integrated with Google Ads.
- Benefits: Great for finding relevant keywords and understanding search trends.
- Ahrefs Keywords Explorer
- Features: Extensive keyword data, including search volume, keyword difficulty, and click metrics. It also provides keyword ideas and SERP analysis.
- Benefits: Comprehensive tool for in-depth keyword research and competitive analysis.
- SEMrush Keyword Magic Tool
- Features: Offers keyword suggestions, search volume, keyword difficulty, and competitive density. It also includes a keyword grouping feature.
- Benefits: Excellent for discovering new keywords and organizing them into relevant groups.
- Ubersuggest
- Features: Provides keyword ideas, search volume, and SEO difficulty. It also offers content ideas and backlink data.
- Benefits: User-friendly and cost-effective tool for keyword research and SEO insights.
SEO Analysis Tools
- Google Search Console
- Features: Monitors site performance, identifies indexing issues, and provides data on search traffic and user behavior.
- Benefits: Essential for understanding how Google interacts with your site and identifying areas for improvement.
- Ahrefs Site Audit
- Features: Comprehensive site audit tool that checks for over 100 SEO issues, including broken links, duplicate content, and slow loading times.
- Benefits: Detailed insights and actionable recommendations for improving site health.
- SEMrush Site Audit
- Features: Conducts site audits to identify and fix on-page SEO issues. It provides a health score and detailed reports on errors, warnings, and notices.
- Benefits: Helps prioritize SEO tasks and track improvements over time.
- Screaming Frog SEO Spider
- Features: Crawls websites to analyze on-page SEO elements, such as meta tags, headers, images, and links. It also identifies broken links and duplicate content.
- Benefits: Powerful desktop tool for in-depth site audits and real-time analysis.
Content Optimization Tools
- Yoast SEO (WordPress Plugin)
- Features: Offers content analysis, keyword optimization, readability scores, and suggestions for internal linking. It also provides tools for optimizing meta tags and generating XML sitemaps.
- Benefits: Comprehensive tool for optimizing WordPress content and improving on-page SEO.
- Surfer SEO
- Features: Analyzes top-ranking pages and provides recommendations for content optimization, including keyword density, content length, and LSI keywords.
- Benefits: Data-driven insights for optimizing content to match search intent and outperform competitors.
- Grammarly
- Features: Checks for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors. It also offers style and readability suggestions.
- Benefits: Ensures content is clear, engaging, and error-free, improving user experience and readability.
- Hemingway Editor
- Features: Highlights complex sentences, passive voice, and readability issues. It provides a readability grade level and suggests improvements.
- Benefits: Helps create concise, readable, and engaging content that appeals to users and search engines.
Using the right tools and resources for on-page SEO can streamline your optimization efforts and ensure you’re following best practices. Keyword research tools help identify relevant keywords, SEO analysis tools provide insights into site performance, and content optimization tools enhance content quality and structure. By leveraging these tools, you can improve your site’s search engine rankings and user experience.
Conclusion
On-page SEO is the foundation of any successful digital marketing strategy. By optimizing individual elements of your web pages, you can significantly improve your site’s visibility in search engine results, enhance user experience, and drive more organic traffic. Implementing best practices for on-page SEO ensures that your content is accessible, relevant, and valuable to both users and search engines.
Recap of Key Points
- Understanding On-Page SEO:
- On-page SEO involves optimizing elements within your website to improve search engine rankings and user experience.
- Key Elements of On-Page SEO:
- Content Quality and Structure: High-quality, relevant content and a logical structure enhance readability and SEO.
- Keyword Research and Integration: Proper keyword research and natural placement within content are essential for relevance and ranking.
- Meta Tags Optimization: Effective title tags and meta descriptions improve visibility and click-through rates.
- Internal Linking: Strategic internal linking improves site navigation and distributes link equity.
- Image Optimization: Optimizing images for speed and SEO improves load times and accessibility.
- URL Structure: Clean, descriptive URLs help search engines and users understand page content.
- Common On-Page SEO Mistakes: Avoiding keyword stuffing, neglecting meta descriptions, poor content quality, and broken links is crucial.
- Tools and Resources:
- Utilizing keyword research, SEO analysis, and content optimization tools can streamline your on-page SEO efforts.
Next Steps for Improving On-Page SEO
- Conduct an SEO Audit:
- Use tools like Google Search Console, Ahrefs Site Audit, or SEMrush Site Audit to identify and fix on-page SEO issues.
- Optimize Content:
- Create high-quality, informative content that satisfies user intent. Use tools like Yoast SEO, Surfer SEO, and Grammarly to enhance content quality and readability.
- Implement Keyword Research:
- Use keyword research tools like Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, or SEMrush to find relevant keywords and integrate them naturally into your content.
- Improve Meta Tags:
- Write compelling and keyword-rich title tags and meta descriptions for each page to improve visibility and click-through rates.
- Enhance Internal Linking:
- Review and update internal links to ensure they are relevant and provide value. Use descriptive anchor text to improve context.
- Optimize Images:
- Compress images, use appropriate file formats, and add descriptive alt text to improve site speed and accessibility.
- Refine URL Structure:
- Create clean, descriptive, and keyword-rich URLs. Avoid unnecessary parameters and maintain a logical hierarchy.
- Avoid Common Mistakes:
- Ensure you’re not keyword stuffing, ignoring meta descriptions, producing poor content, or leaving broken links unfixed.
By taking these actionable steps, you can enhance your on-page SEO, boost your search engine rankings, and provide a better user experience. Consistently applying best practices and regularly reviewing your SEO efforts will lead to long-term success and growth for your website.








