The Cookieless Future and First-Party Data Strategies: A Comprehensive Guide
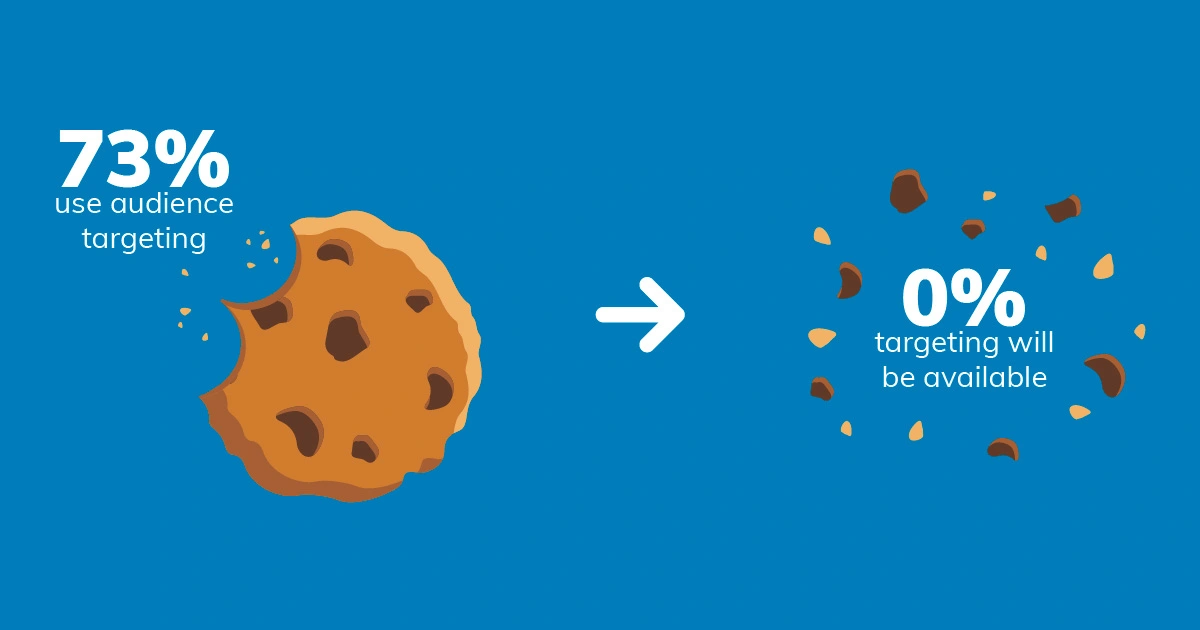
With the impending phase-out of third-party cookies by 2024, the digital marketing landscape is set for a revolutionary change. Marketers must prepare for a world where first-party data is crucial to understanding and engaging customers, requiring new methods that prioritize privacy, consent, and customer trust.

This guide covers the impact of the cookieless future, why first-party data is essential, and actionable strategies to collect, manage, and use first-party data for success.
Introduction to the Cookieless Future
The end of third-party cookies marks a significant shift in digital marketing. These cookies, which track users across the internet to enable targeted advertising, will no longer be available by 2024. This move aligns with growing privacy concerns and stricter regulations like the GDPR and CCPA, which emphasize user consent and data transparency.
As a result, marketers must now rely on first-party data gathered from their own interactions with customers. This cookieless world challenges businesses to build direct relationships, fostering trust while respecting customer privacy.
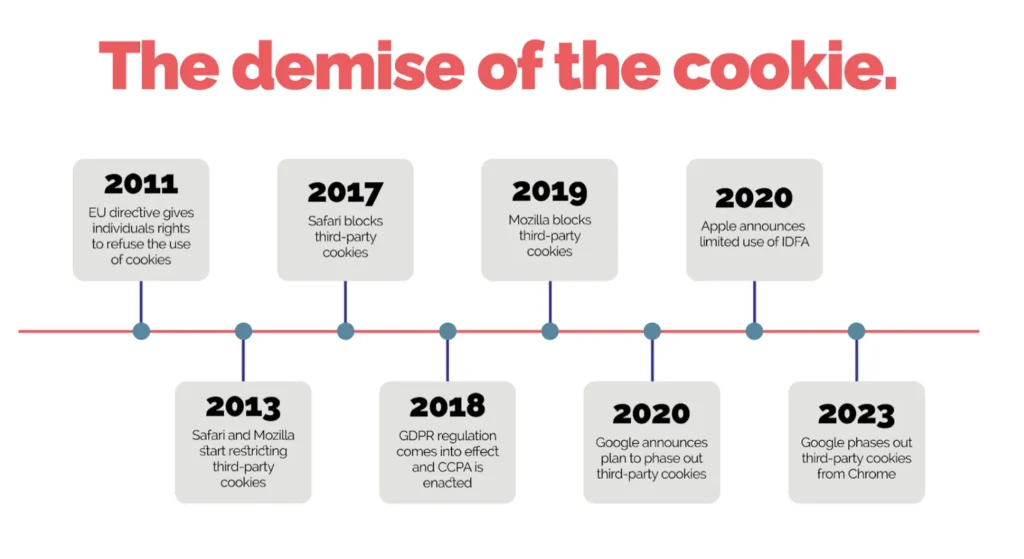
Understanding the Decline of Third-Party Cookies
For years, third-party cookies have been a cornerstone of digital advertising, enabling businesses to track user behavior across multiple websites. However, mounting concerns over privacy, data misuse, and lack of consent have led tech giants and regulatory bodies to restrict or eliminate these tracking tools.
Key Reasons for the Shift:
- User Privacy: Consumers are more aware of how their data is used, driving demand for privacy-focused alternatives.
- Regulatory Pressure: Laws like GDPR in Europe and CCPA in California require companies to be transparent about data collection.
- Browser Restrictions: Browsers like Safari and Firefox have already blocked third-party cookies, with Google Chrome set to follow by 2024.
As a result, businesses must pivot to first-party data strategies that respect user privacy and adhere to legal requirements.

Why First-Party Data Matters in a Cookieless World
First-party data is data collected directly from customers through a company’s owned channels, such as websites, apps, and in-store interactions. This data is increasingly valuable because it’s accurate, privacy-compliant, and strengthens brand-customer relationships. Key benefits include:
- Reliability and Relevance: Data gathered directly from customers is typically more accurate and relevant.
- Enhanced Customer Trust: Businesses that prioritize user consent and transparency foster trust and brand loyalty.
- Compliance with Regulations: First-party data aligns with GDPR, CCPA, and other data protection laws, reducing compliance risks.
Key Methods for Collecting First-Party Data
In a cookieless environment, first-party data collection becomes the primary tool for gathering insights on user behavior. Effective methods include:
- Email and Newsletter Signups: Encouraging customers to subscribe allows brands to collect emails and segment audiences based on their interests and engagement.
- Loyalty Programs and Rewards: Loyalty programs incentivize users to provide data while fostering long-term relationships.
- Website and App Behavior Tracking: Collect data on user interactions within owned digital properties, like site navigation and app usage.
- Customer Surveys and Feedback: Directly asking users for feedback can provide valuable insights into preferences and satisfaction.
These methods offer ethical and effective ways to gather insights without violating user privacy.
Developing a First-Party Data Strategy
A first-party data strategy is essential for capturing, organizing, and leveraging customer insights. Building a strategy involves the following steps:
- Define Data Collection Goals: Clarify what information is necessary to achieve your business objectives.
- Select the Right Tools and Platforms: Consider Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) to store and analyze data.
- Integrate Data Across Channels: Ensure all customer data from websites, emails, and apps is unified for a comprehensive view.
- Prioritize Consent and Transparency: Communicate clearly about data use, respecting user preferences.
A well-planned first-party data strategy enables brands to build comprehensive customer profiles while respecting privacy.
Integrating CRM Systems for Data Collection
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems are invaluable in a cookieless world, allowing brands to organize and analyze first-party data efficiently. CRM systems help businesses centralize data from multiple channels, creating a single source of truth for customer insights.
Benefits of CRM in First-Party Data Strategies:
- Centralized Customer Profiles: Store detailed customer data to support targeted marketing.
- Streamlined Data Access Across Teams: Allows sales, marketing, and support teams to access the same data.
- Improved Personalization: Use CRM data to tailor marketing messages based on a customer’s past interactions.
- Image Suggestion: Screenshot of CRM dashboard showcasing customer profiles.
Leveraging Email Marketing for First-Party Data
Email marketing offers a direct line to consumers, making it one of the most effective methods for collecting and leveraging first-party data. Through email campaigns, brands can gather insights into customer engagement, segment audiences, and optimize content based on user preferences.
- Segment Audiences by Behavior: Group subscribers based on actions, preferences, or demographics.
- Personalize Content Using Engagement Data: Tailor content to users’ behavior, such as purchase history or page views.
- Analyze Key Metrics: Open rates, click-through rates, and bounce rates provide insights into user engagement and content effectiveness.
Enhancing Personalization Through First-Party Data
Personalization drives customer satisfaction, loyalty, and engagement. First-party data enables brands to customize interactions, whether through personalized recommendations or dynamic website content.
- Customized Website Content: Tailor homepage banners and suggested products based on a user’s browsing history.
- Dynamic Product Recommendations: Show relevant products based on purchase history or previous interest.
- Real-Time Notifications: Use first-party data to trigger personalized notifications when users visit a website or app.
Building Loyalty Programs for Data Collection
Loyalty programs are powerful tools for building a long-term connection with customers while collecting valuable first-party data. These programs can provide insights into customer habits, preferences, and loyalty levels.
- Behavioral Insights: Track purchase frequency, average spend, and preferred products.
- Data Collection Over Time: Loyalty programs encourage consistent engagement, allowing brands to collect data regularly.
- Incentivized Data Sharing: Rewards encourage customers to provide insights in exchange for points or perks.
Ensuring Compliance with Privacy Regulations
Privacy laws like GDPR and CCPA mandate that businesses collect and use data responsibly, prioritizing user consent and data transparency. To remain compliant, brands should:
- Obtain Explicit Consent: Ensure users understand and agree to data collection practices.
- Communicate Data Use: Clearly explain how collected data will be used, stored, and protected.
- Provide Opt-Out Options: Make it easy for users to change their consent preferences.
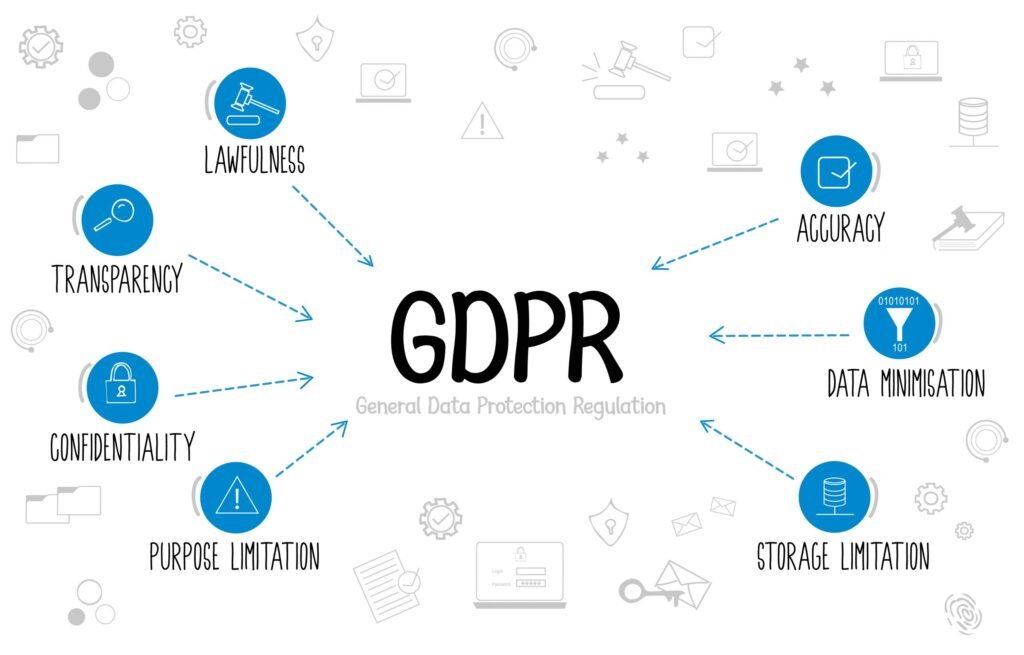
Following these guidelines builds trust with users and reduces the risk of regulatory penalties.
Measuring the ROI of First-Party Data Efforts
Tracking the effectiveness of first-party data strategies is essential for understanding their impact. Key performance indicators (KPIs) include:
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): Measures the total revenue generated from a customer over their lifetime.
- Engagement Metrics: Tracks user interaction with content, such as click-through rates, time on page, and bounce rates.
- Retention Rates: Measures the ability to retain customers over time, often tied to effective loyalty and engagement strategies.
Challenges in Transitioning to First-Party Data Models
Transitioning to first-party data presents challenges, such as data integration and ensuring data quality. Common issues include:
- Data Silos: Data stored in isolated systems can hinder a complete view of customer behavior.
- Compliance with Privacy Laws: Managing user consent across different data sources can be complex.
- Limited Data on New Users: First-party data provides rich insights but may lack information on new or unknown users.
Overcoming these challenges requires careful planning, the right technology, and a commitment to transparency.
Key Trends Shaping First-Party Data and Marketing
Emerging technologies and strategies are reshaping how businesses use first-party data, including:
- AI and Machine Learning: These tools analyze data patterns, enabling predictive marketing and more refined segmentation.
- Increased Use of Interactive Marketing: Engaging users through personalized experiences like quizzes and polls encourages data sharing.
- Consent-Driven Marketing: With privacy concerns on the rise, consent-driven marketing is becoming the new standard for trust-building.
- Image Suggestion: AI and machine learning data visualization.
Actionable Steps for Adopting First-Party Data
- Adopt a Comprehensive CRM System: Store and organize data in a way that provides a single customer view.
- Conduct a Privacy Compliance Audit: Ensure your data collection practices comply with relevant privacy laws.
- Train Teams on Data Ethics and Privacy: Educate employees on the importance of user consent and data privacy.
Case Studies: First-Party Data in Action
Case Study 1: Retail Brand Loyalty Program A major retail brand launched a loyalty program to collect customer insights. By offering personalized discounts and rewards, they increased repeat purchases by 30% and gained valuable data on purchase preferences.
Case Study 2: Streaming Service Email Segmentation A streaming platform segmented its email subscribers based on viewing history. By personalizing email recommendations, they improved click-through rates by 50%, leading to a substantial increase in subscriptions.
Case Study 3: Financial Services Personalized Content A financial services company used CRM to personalize website content for returning users. This increased engagement time on the site by 40% and led to a higher conversion rate for premium services.
FAQs on the Cookieless Future and First-Party Data

- What is the cookieless future? The cookieless future refers to the digital environment that no longer relies on third-party cookies for user tracking, focusing on privacy and consent.
- Why is first-party data essential? First-party data is collected directly from users, offering accurate insights that are privacy-compliant and reliable.
- How can businesses start collecting first-party data? Start with owned channels like email signups, loyalty programs, and customer feedback surveys.
- What are CRM systems’ roles in first-party data strategies? CRM systems store and analyze customer data across channels, enabling a unified approach to customer insights.
- How do privacy laws impact first-party data collection? Laws like GDPR and CCPA require transparency and consent in data practices, fostering trust and reducing legal risks.
- How will the phase-out of third-party cookies affect ad targeting?
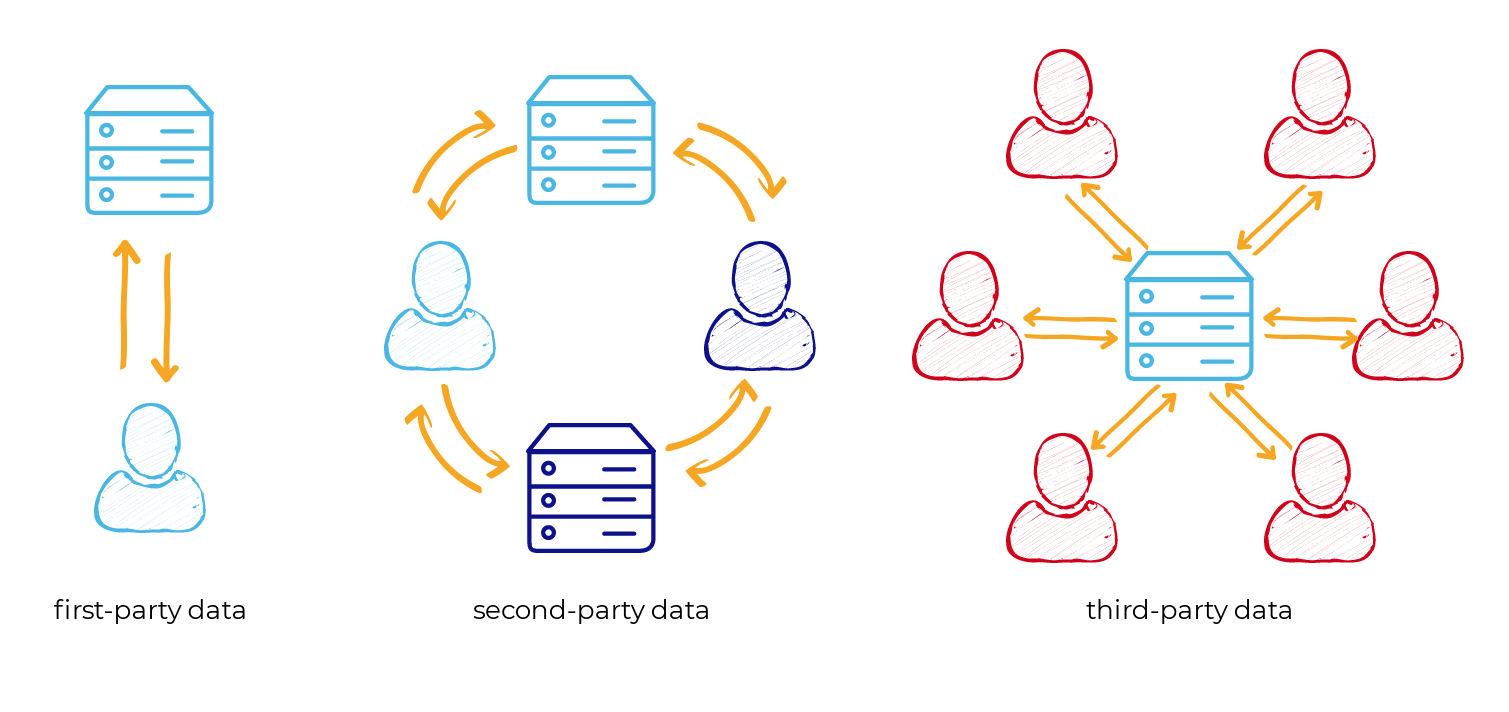
Without third-party cookies, brands will have to rely on first-party data, contextual targeting, and other privacy-compliant methods to reach specific audiences. - What’s the difference between first-party data and second-party data?
First-party data is collected directly from a brand’s interactions with customers. Second-party data, on the other hand, is shared by another organization (such as a trusted partner) but still originates from direct customer interactions. - How can I ensure my first-party data strategy is scalable?
Invest in robust data management platforms like CRM and CDP systems, and use standardized data-collection methods to ensure scalability as your customer base grows. - Are there alternatives to cookies for tracking user behavior?
Yes, alternatives include first-party cookies, server-side tracking, and contextual targeting, which deliver insights while respecting user privacy. - What are the most common challenges with first-party data collection?
Key challenges include managing data integration across multiple platforms, ensuring data quality, and gaining explicit user consent for compliant data practices.
Conclusion: Preparing for a Data-Driven Future
In a cookieless world, businesses must prioritize first-party data strategies that respect user privacy and build long-lasting relationships. By focusing on transparency, consent, and personalized engagement, companies can turn these changes into opportunities, ensuring long-term growth and success.
Disclosure: Our blog contains affiliate links to products. We may receive a commission for purchases made through these links. However, this does not impact our reviews and comparisons. We try our best to keep things fair and balanced, in order to help you make the best choice for you.